- Defend & Conquer
- Posts
- Building effective governance models for fourth-party cyber risk management
Building effective governance models for fourth-party cyber risk management
CybersecurityHQ Report - Pro Members

Welcome reader to a 🔒 pro subscriber-only deep dive 🔒.
Brought to you by:
👣 Smallstep – Secures Wi-Fi, VPNs, ZTNA, SaaS and APIs with hardware-bound credentials powered by ACME Device Attestation
🏄♀️ Upwind Security – Real-time cloud security that connects runtime to build-time to stop threats and boost DevSecOps productivity
🔧 Endor Labs – App security from legacy C++ to Bazel monorepos, with reachability-based risk detection and fix suggestions across the SDLC
📊 LockThreat – AI-powered GRC that replaces legacy tools and unifies compliance, risk, audit and vendor management in one platform
🧠 Ridge Security – The AI-powered offensive security validation platform
Forwarded this email? Join 70,000 weekly readers by signing up now.
#OpenToWork? Try our AI Resume Builder to boost your chances of getting hired!
—
Get lifetime access to our deep dives, weekly cyber intel podcast report, premium content, AI Resume Builder, and more — all for just $799. Corporate plans are now available too.
Executive Summary
Fourth-party cyber risk represents one of the most significant and overlooked vulnerabilities in modern enterprise security. While organizations have invested heavily in managing direct vendor relationships, the vendors of those vendors often operate in the shadows, creating cascading risks that can devastate operations, compromise sensitive data, and trigger regulatory penalties. This whitepaper provides Chief Information Security Officers and risk management professionals with actionable frameworks for governing fourth-party cyber risks in 2025's increasingly interconnected digital ecosystem.
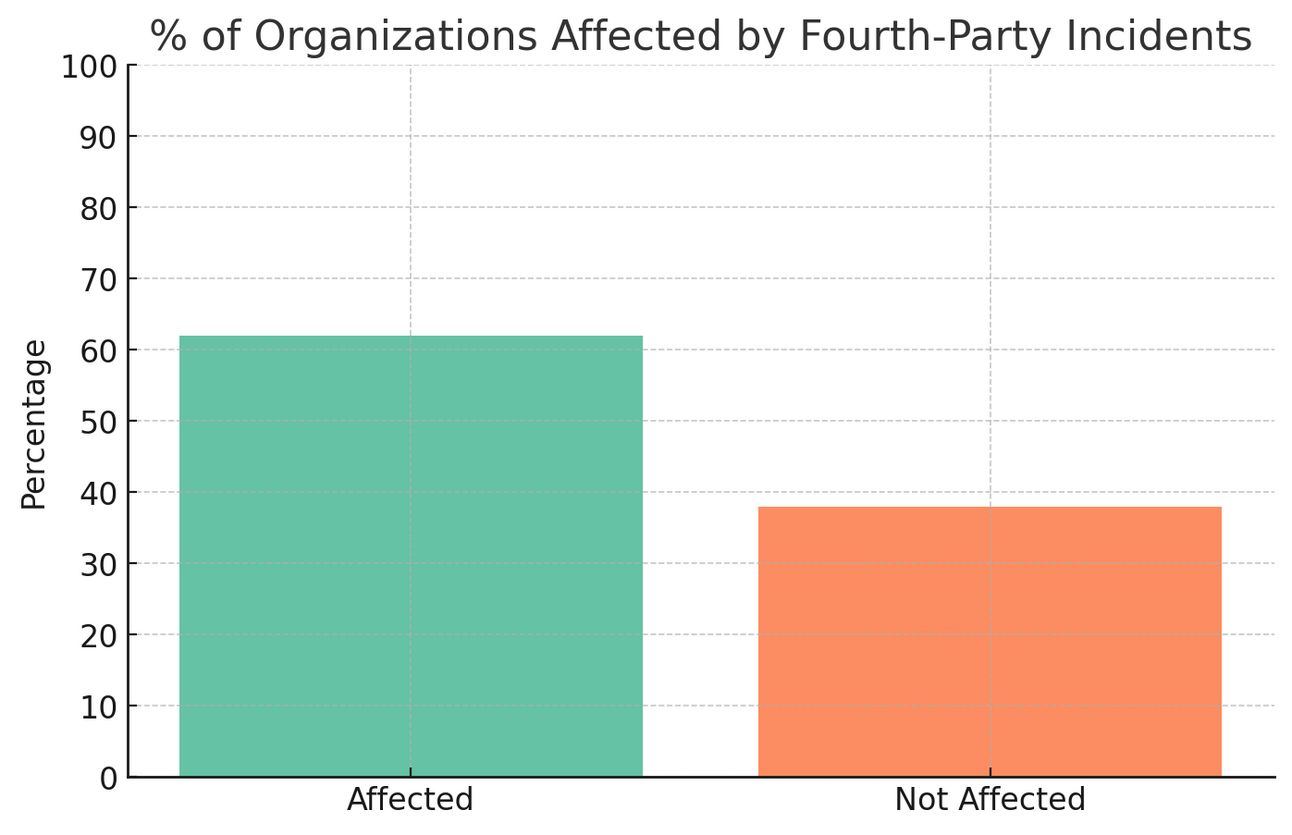
Recent incidents underscore the urgency: the 2023 MOVEit breach affected hundreds of organizations through their vendors' use of compromised file transfer software, while the 2024 CrowdStrike update failure demonstrated how a single fourth-party can simultaneously disrupt airlines, hospitals, and financial institutions globally. With 62% of organizations experiencing supply chain cyber disruptions in the past year and regulators imposing stricter accountability through frameworks like DORA and NIS2, effective fourth-party governance has evolved from best practice to business imperative.
This whitepaper examines proven governance strategies across multiple industries, drawing on empirical research, regulatory developments, and real-world case studies. Key findings include the critical importance of CEO-level oversight, the necessity of fundamentally redesigning workflows to accommodate fourth-party risk management, and the emergence of continuous monitoring technologies that provide real-time visibility into extended supply chains. We present a comprehensive governance model incorporating risk assessment frameworks, contractual mechanisms, technology enablement, and organizational structures that balance centralized control with distributed execution.

Subscribe to CybersecurityHQ Newsletter to unlock the rest.
Become a paying subscriber of CybersecurityHQ Newsletter to get access to this post and other subscriber-only content.
Already a paying subscriber? Sign In.
A subscription gets you:
- • Access to Deep Dives and Premium Content
- • Access to AI Resume Builder
- • Access to the Archives
Reply