- Defend & Conquer
- Posts
- Machine identity & certificate sprawl management in dynamic environments
Machine identity & certificate sprawl management in dynamic environments
CybersecurityHQ Report - Pro Members

Welcome reader to a 🔒 pro subscriber-only deep dive 🔒.
Brought to you by:
👣 Smallstep – Secures Wi-Fi, VPNs, ZTNA, SaaS and APIs with hardware-bound credentials powered by ACME Device Attestation
📊 LockThreat – AI-powered GRC that replaces legacy tools and unifies compliance, risk, audit and vendor management in one platform
Forwarded this email? Join 70,000 weekly readers by signing up now.
#OpenToWork? Try our AI Resume Builder to boost your chances of getting hired!
—
Get lifetime access to our deep dives, weekly cyber intel podcast report, premium content, AI Resume Builder, and more — all for just $799. Corporate plans are now available too.
Executive Summary
Machine identities now outnumber human identities by ratios exceeding 80:1 in many enterprises, creating an exponential governance challenge that threatens both operational resilience and security posture.¹ Unlike human identities, these non-human credentials—TLS certificates, API keys, service accounts, and cryptographic keys—proliferate rapidly across hybrid cloud environments, often beyond the visibility of traditional identity and access management systems.
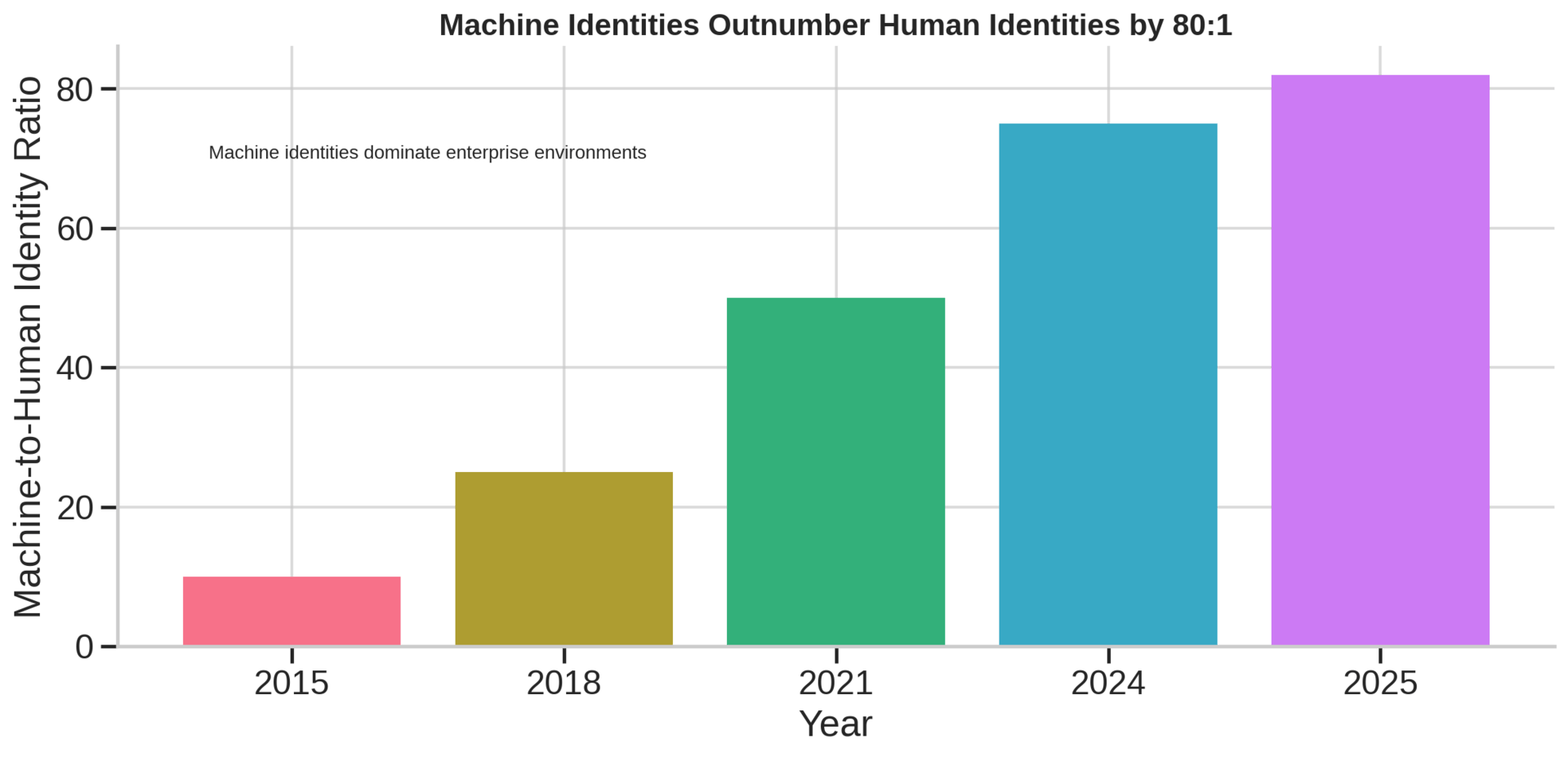
The stakes have never been higher. Recent high-profile incidents demonstrate how certificate mismanagement triggers cascading failures: SpaceX Starlink's global outage from an expired ground station certificate, Microsoft Azure's multi-hour Teams disruption due to certificate misconfiguration, and the UK's CHAPS financial system halt from an expired SSL certificate.² Each incident cost millions in direct losses and reputational damage, yet represented entirely preventable failures of governance rather than sophisticated attacks.
Security breaches involving compromised machine credentials now account for 38 percent of all data breaches, surpassing phishing and malware as the primary attack vector.³ The Storm-0558 incident exemplified this threat: Chinese state actors used a stolen Microsoft signing key to forge authentication tokens, accessing U.S. government email accounts for months undetected.⁴ The key had been inadvertently exposed in a crash dump two years earlier, illustrating how poor machine identity lifecycle management creates persistent vulnerabilities.
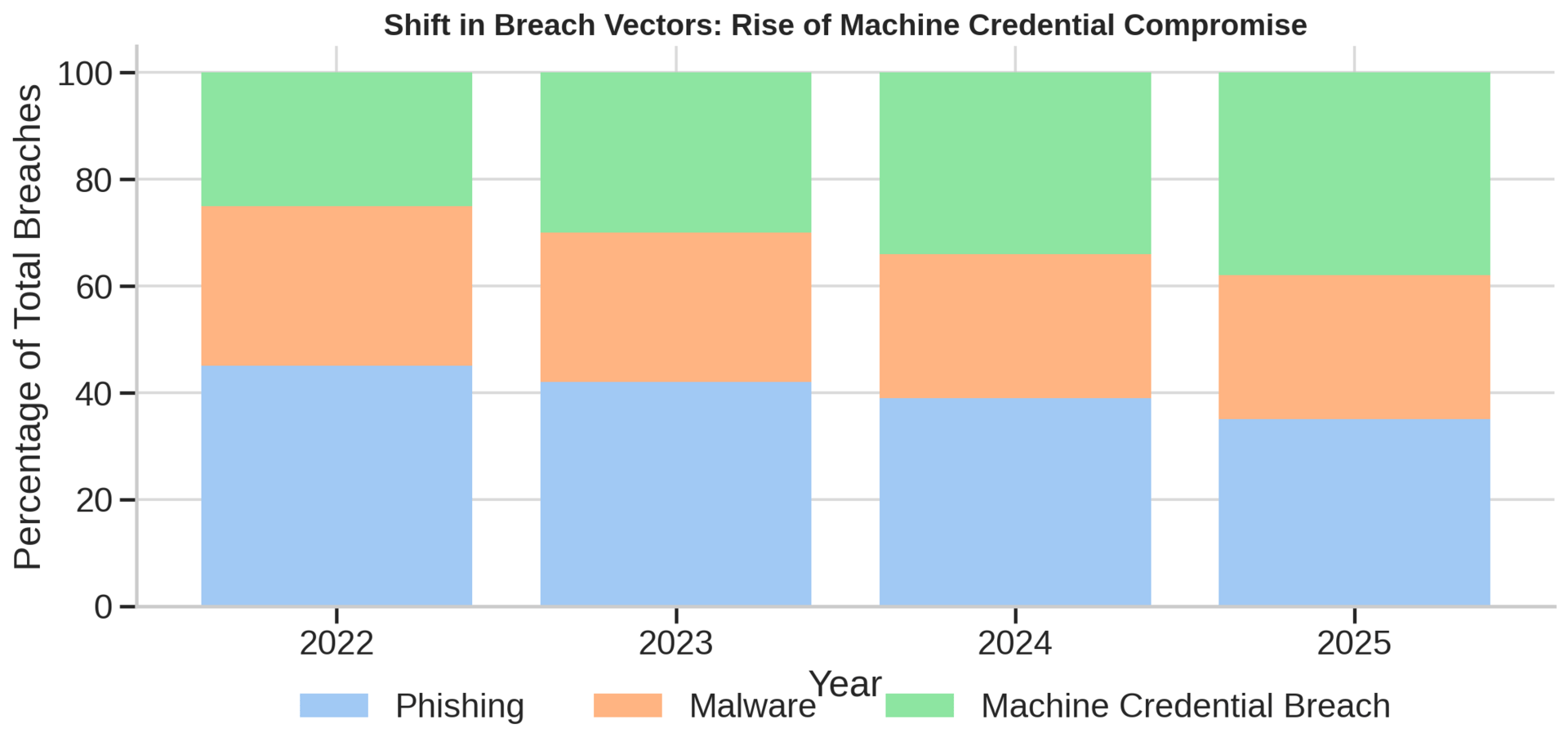
Regulatory frameworks are hardening around machine identity controls. ISO 27001:2022 now explicitly mandates lifecycle management for non-human identities through Annex A.5.16, while the EU's Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) requires financial institutions to address cryptographic asset management as part of ICT risk controls.⁵ Organizations failing to demonstrate robust certificate and key governance face both compliance penalties and exclusion from regulated markets.
This whitepaper synthesizes insights from 2024-2025 threat intelligence, regulatory guidance, and enterprise implementations to provide CISOs with a strategic framework for addressing machine identity sprawl. Key findings include:
Automation is non-negotiable. Organizations that have fundamentally redesigned workflows around certificate lifecycle management report 30 percent reduction in breach risk and elimination of certificate-related outages.⁶ Manual renewal processes cannot scale to handle certificates with 90-day or shorter lifespans, which major browser vendors are mandating by 2027.
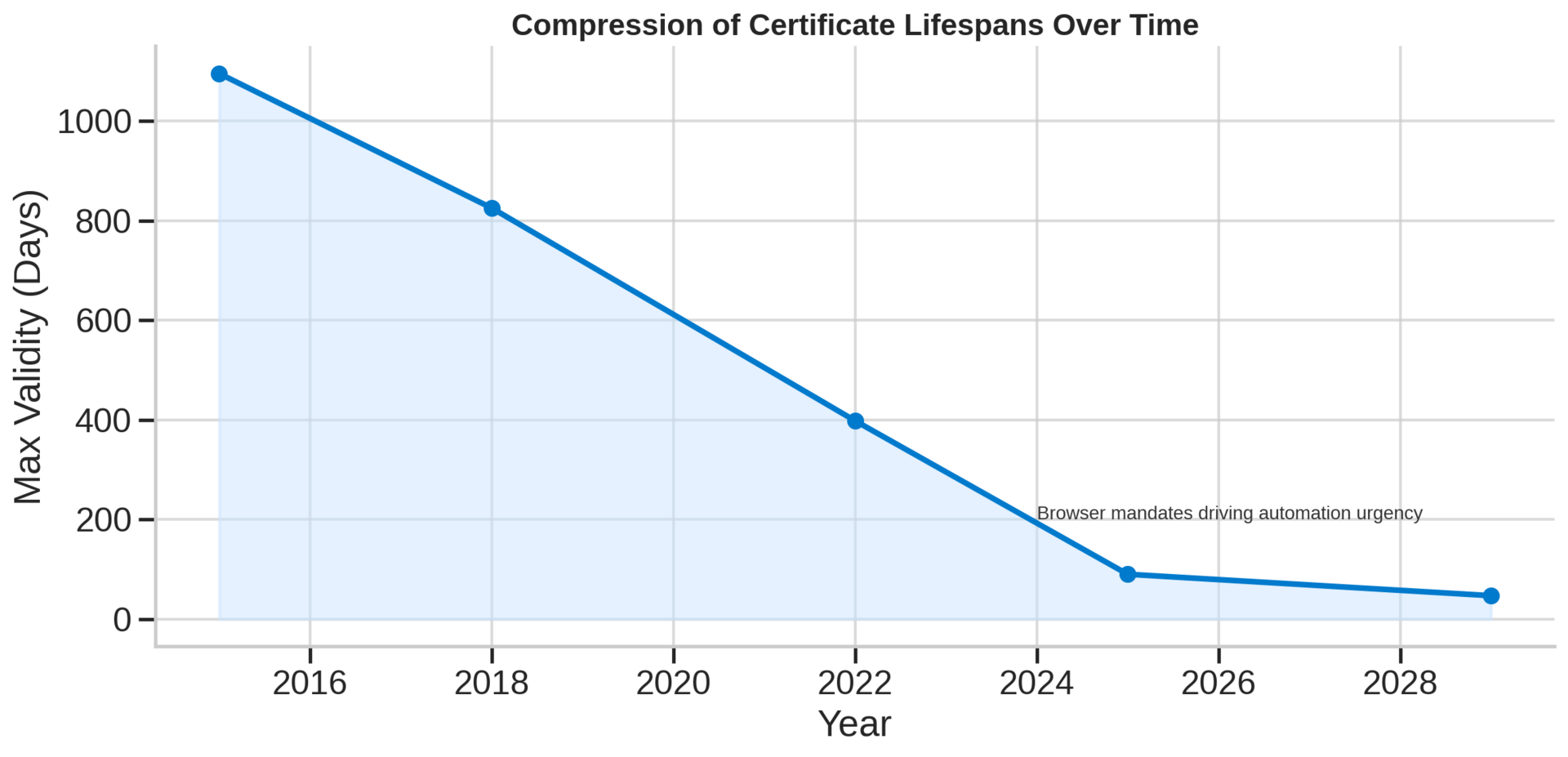
Executive ownership drives value. Our analysis shows CEO oversight of AI and identity governance correlates most strongly with reported bottom-line impact from technology deployments.⁷ Organizations where the board or C-suite directly oversees machine identity governance implement controls more consistently and recover faster from incidents.
Risk stratification enables focused investment. Not all machine identities carry equal impact. Certificates protecting customer PII, financial transactions, or code-signing operations merit far stricter controls than test system credentials. Leading organizations classify machine identities by business criticality and data sensitivity, applying layered protections to high-value assets.
Zero Trust requires machine identity integration. NIST SP 800-207 mandates dynamic policy-driven access for all entities, including non-human identities.⁸ Static, long-lived machine credentials fundamentally violate Zero Trust principles. Effective implementation requires just-in-time provisioning, continuous authorization, and integration of certificate validation into policy decision points.
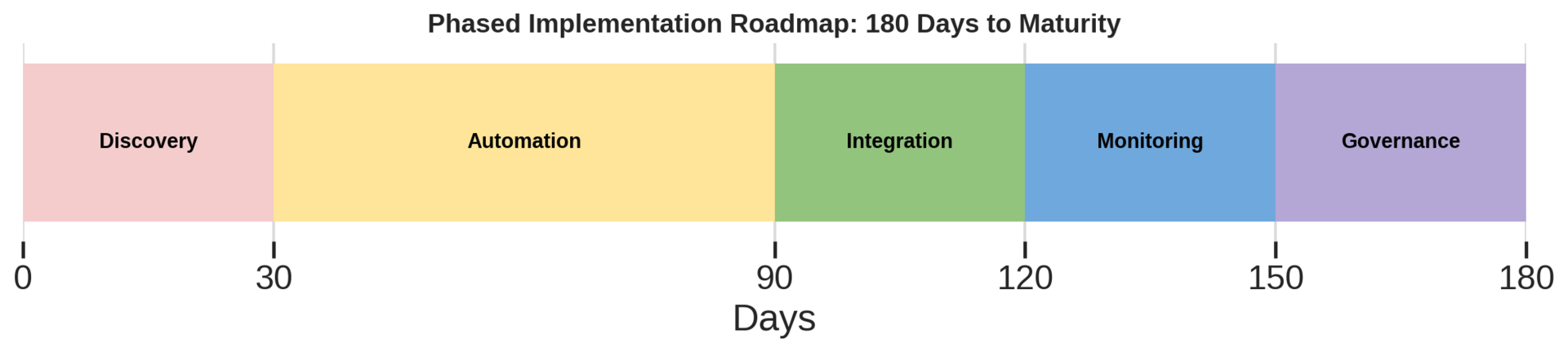
The path forward requires phased transformation rather than point solutions. Organizations capturing meaningful value follow a 180-day roadmap: comprehensive discovery and inventory in the first 30 days, deployment of centralized certificate lifecycle management and secrets vaults by day 90, and enterprise-wide automation with zero-trust integration by day 180. This approach delivers quick wins—preventing imminent expirations—while building sustainable governance capabilities.

Subscribe to CybersecurityHQ Newsletter to unlock the rest.
Become a paying subscriber of CybersecurityHQ Newsletter to get access to this post and other subscriber-only content.
Already a paying subscriber? Sign In.
A subscription gets you:
- • Access to Deep Dives and Premium Content
- • Access to AI Resume Builder
- • Access to the Archives
Reply