- Defend & Conquer
- Posts
- Quantifying risk from prompt-based data exfiltration
Quantifying risk from prompt-based data exfiltration
CybersecurityHQ Report - Pro Members

Welcome reader to a 🔒 pro subscriber-only deep dive 🔒.
Brought to you by:
👣 Smallstep – Secures Wi-Fi, VPNs, ZTNA, SaaS and APIs with hardware-bound credentials powered by ACME Device Attestation
📊 LockThreat – AI-powered GRC that replaces legacy tools and unifies compliance, risk, audit and vendor management in one platform
Forwarded this email? Join 70,000 weekly readers by signing up now.
#OpenToWork? Try our AI Resume Builder to boost your chances of getting hired!
—
Get lifetime access to our deep dives, weekly cyber intel podcast report, premium content, AI Resume Builder, and more — all for just $799. Corporate plans are now available too.
Executive Summary
Prompt-based data exfiltration (PBDE) has emerged as the defining security vulnerability of the generative AI era, combining the stealth of social engineering with the automation of technical exploits. Organizations deploying large language models in enterprise workflows face a new class of attacks where adversarial inputs manipulate AI systems into revealing or transmitting sensitive information. Unlike traditional data breaches, PBDE exploits the fundamental ambiguity in how LLMs process natural language, blurring the distinction between legitimate queries and malicious commands.
The financial stakes are substantial and rising. Global data breach costs reached $4.88 million in 2024, representing a 10 percent increase year-over-year, the steepest jump since the pandemic.¹ For 2025, U.S. organizations face average costs exceeding $10 million per incident, driven by regulatory fines and detection expenses.² Prompt injection now ranks as the number one risk in OWASP's Top 10 for LLM Applications, with multi-turn attacks achieving success rates approaching 93 percent in open-weight models.³
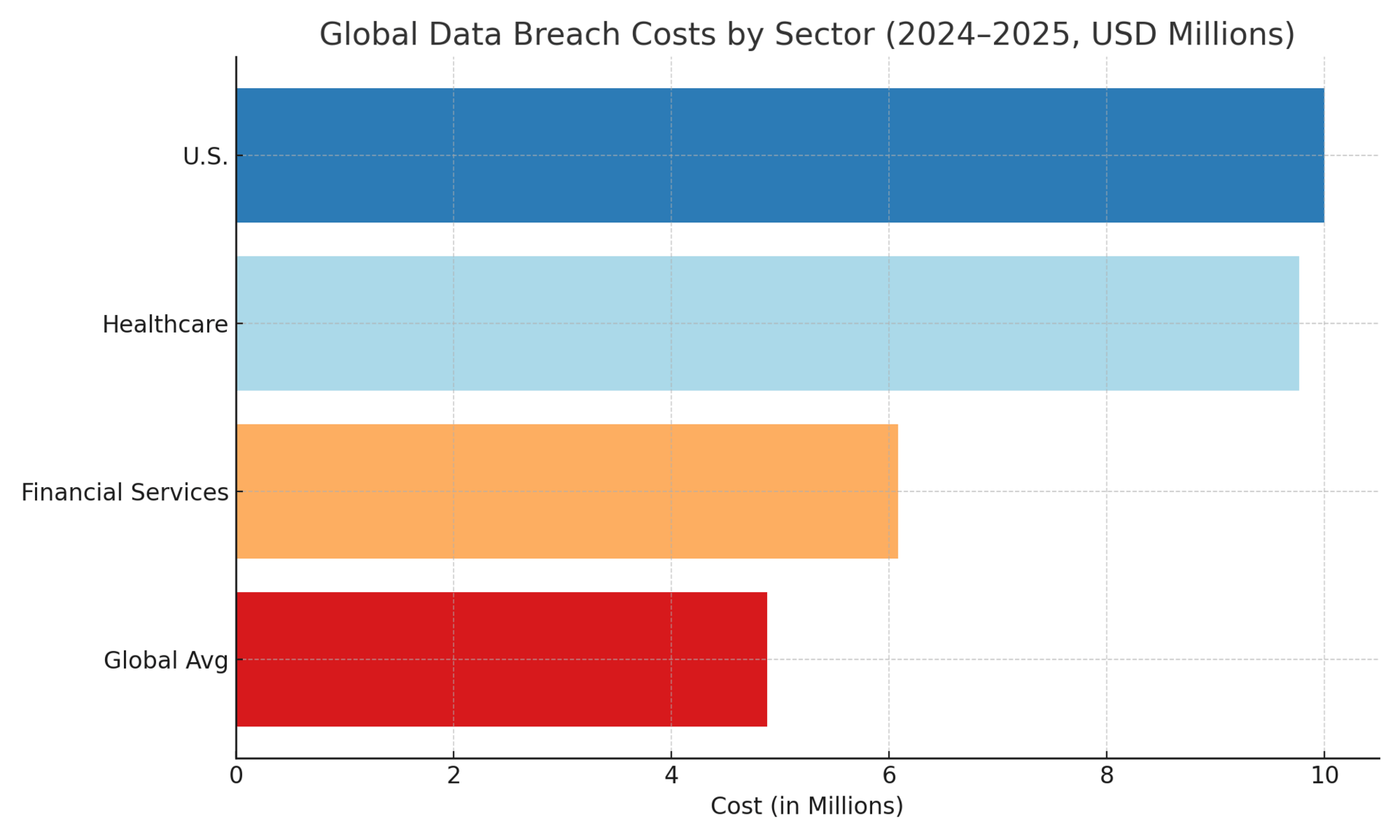
Recent zero-click vulnerabilities underscore the severity. The EchoLeak exploit in Microsoft 365 Copilot and the Mermaid diagram attack vector demonstrated how sophisticated chains of architectural bypasses enable data exfiltration without user interaction.⁴,⁵ Healthcare organizations, already facing the highest breach costs at $9.77 million, confront particular exposure given the sensitivity of patient data and strict HIPAA requirements.⁶ Financial services follow closely at $6.08 million per breach, reflecting stringent regulatory oversight and the value of customer records.⁷
This guide provides CISOs with frameworks to quantify PBDE risk in financial terms using Factor Analysis of Information Risk (FAIR) methodologies, implement defense-in-depth architectures aligned with ISO 42001 and NIST AI RMF standards, and establish governance structures that balance innovation velocity with risk mitigation. Organizations that fail to implement quantitative risk management and architectural controls will face not only direct breach costs but cascading impacts to market valuation, competitive position, and stakeholder trust.

Subscribe to CybersecurityHQ Newsletter to unlock the rest.
Become a paying subscriber of CybersecurityHQ Newsletter to get access to this post and other subscriber-only content.
Already a paying subscriber? Sign In.
A subscription gets you:
- • Access to Deep Dives and Premium Content
- • Access to AI Resume Builder
- • Access to the Archives
Reply