- Defend & Conquer
- Posts
- Hardware security foundations just cracked
Hardware security foundations just cracked
CybersecurityHQ weekly analysis

Welcome reader to your CybersecurityHQ report
Brought to you by:
👣 Smallstep – Secures Wi-Fi, VPNs, ZTNA, SaaS and APIs with hardware-bound credentials powered by ACME Device Attestation
📊 LockThreat – AI-powered GRC that replaces legacy tools and unifies compliance, risk, audit and vendor management in one platform
Forwarded this email? Join 70,000 weekly readers by signing up now.
—
Get annual access to our deep dives, weekly cyber intel podcast report, premium content, AI Resume Builder, and more — all for just $299. Corporate plans are now available too.
Introducing the CISO Access Plan Unlock premium CybersecurityHQ insights at no cost, exclusively for CISOs. Reach out to me to claim your access.
CISO Weekly Tactical Brief: Hardware Security Foundations Crack as TEE.Fail Breaches Confidential Computing While Microsoft WSUS Exploitation and 183M Gmail Breach Expose Verification Gaps
EXECUTIVE DIGEST — For CISOs & Leadership (Stop here if pressed for time)
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
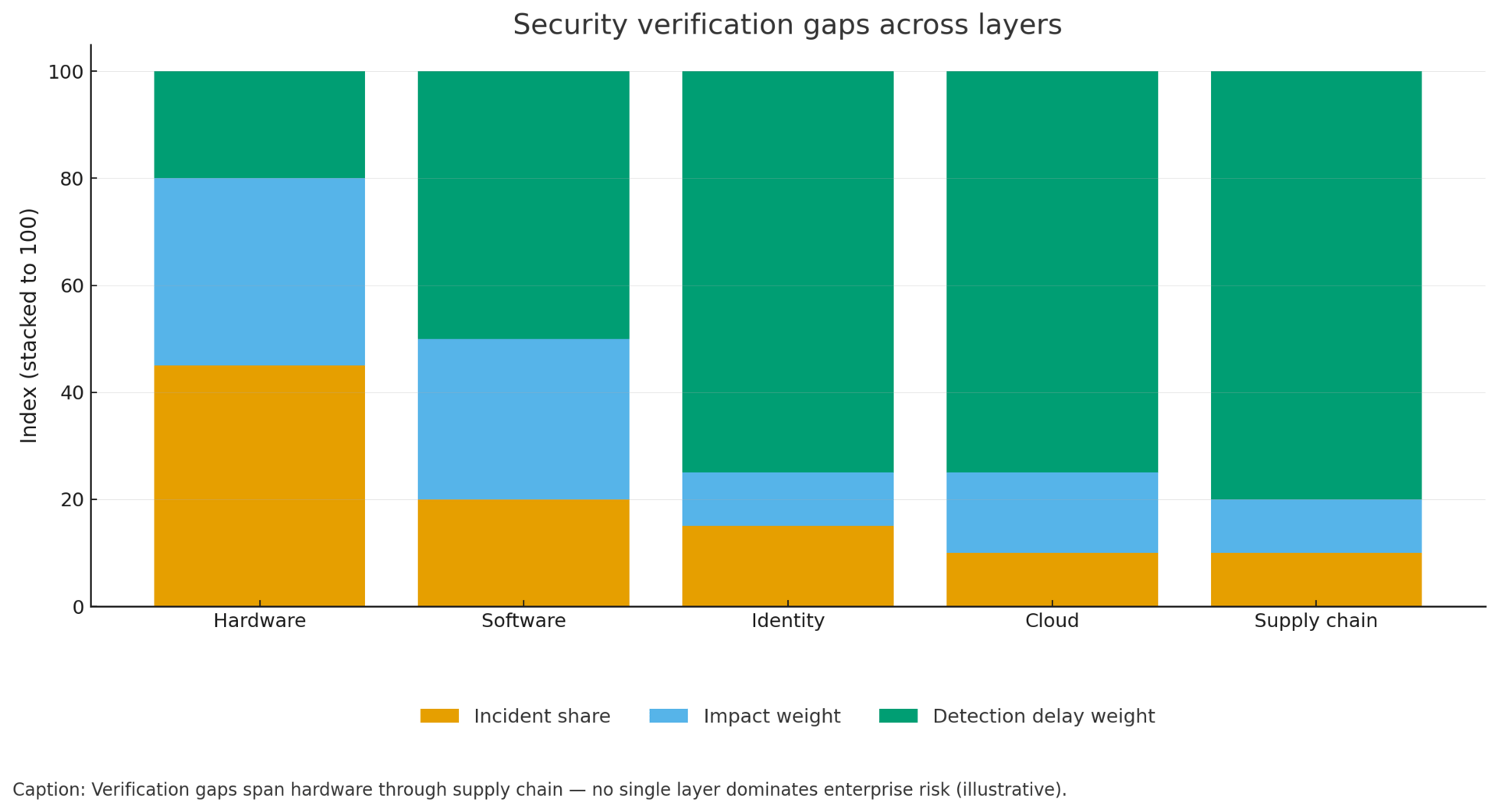
This week exposed security verification gaps across every infrastructure layer, requiring strategic assessment within Q4 reviews rather than emergency response.
Foundation-Level Threats Materialized:
TEE.Fail hardware attack extracts cryptographic keys from Intel, AMD, and Nvidia secure computing environments by exploiting DDR5 memory—bypassing CPU-based security entirely.[1] This threatens $billions in confidential computing investments for regulatory compliance and zero-trust architectures.
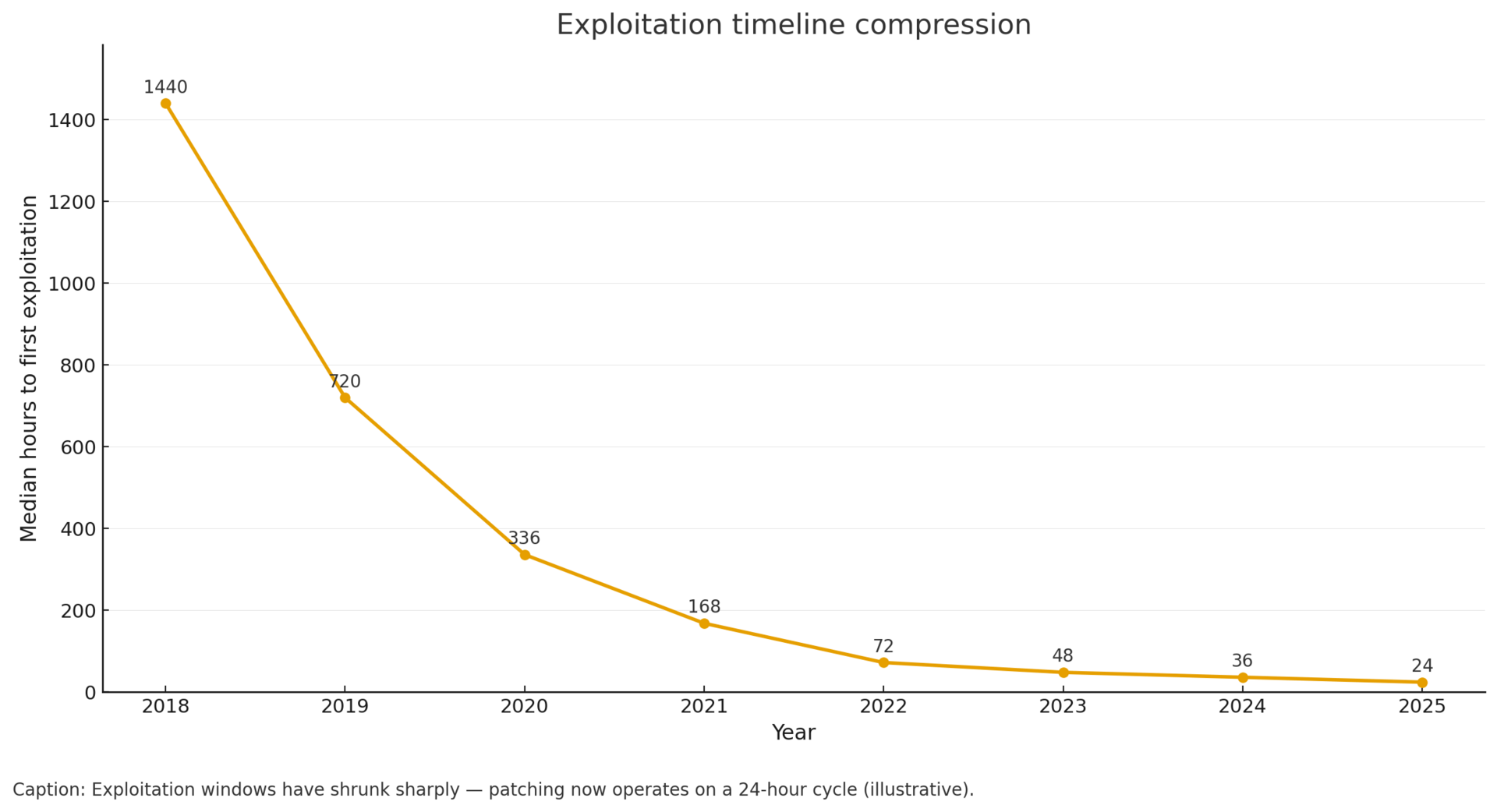
Microsoft WSUS vulnerability (CVE-2025-59287) weaponized within 24 hours of disclosure, with initial patches proving insufficient.[2] Demonstrates compressed exploitation timelines overwhelming traditional patch management.
183 million Gmail passwords leaked via infostealer malware,[3] validating industry shift toward passwordless authentication as credential-based models fail at scale.
Azure outages affecting Office 365, Xbox, and Alaska Airlines—one week after AWS disruption—confirms cloud concentration risk across providers controlling 65% of market share.[4]
Amazon announced 14,000-30,000 job cuts while Meta reduced 600 AI roles,[5] raising vendor workforce continuity questions for critical services.
Immediate Actions (Using Existing Resources):
Inventory confidential computing dependencies to assess TEE.Fail exposure (Target: Complete by Nov 5)
Verify WSUS patches and review network segmentation (Target: 95% deployment by Nov 1)
Enforce MFA and accelerate passwordless pilots using 183M breach as business case (Target: 15% increase in MFA coverage by Nov 15)
Test multi-cloud contingency procedures following dual-provider disruption pattern
Model vendor workforce continuity scenarios for critical suppliers
Resource Strategy: This week requires assessment and acceleration within existing programs, not new budget. Use findings to inform Q1 planning for hardware security architecture, accelerated patch frameworks, passwordless authentication scaling, and multi-cloud resilience investments.
Assessment Advantage: Organizations conducting comprehensive security foundation reviews now position 6-12 months ahead of competitors conducting reactive emergency responses after incidents.
TOP 3 DECISIONS
Priority | Action | Why Now |
|---|---|---|
1 | Hardware security model assessment | TEE.Fail compromises foundational confidential computing assumptions |
2 | WSUS exploitation containment | CVE-2025-59287 under active attack; partial mitigation inadequate |
3 | Credential verification acceleration | 183M Gmail breach demands MFA enforcement and passwordless migration |
CRITICAL NUMBERS
183 million: Gmail passwords in infostealer leak[3]
CVE-2025-59287: Microsoft WSUS vulnerability under active exploitation[2]
14,000-30,000: Amazon corporate job cuts[5]
9 million: Exploit attempts observed in October against critical vulnerabilities[7]
$176M: Crypto regulatory fine demonstrating enforcement escalation
400 million: Europeans at risk from fragmented telecom regulations per Europol[8]
STRATEGIC CONTEXT — For CISOs, Board Members & Executives
STRATEGIC PRIORITIES THIS WEEK
Assess hardware security dependencies within existing infrastructure audits. On October 23-24, researchers disclosed TEE.Fail, a side-channel attack exploiting DDR5 memory to extract cryptographic keys from Intel TDX, AMD SEV-SNP trusted execution environments, and Nvidia's GPU Confidential Computing.[1] This hardware-level compromise bypasses CPU-based security entirely, threatening the foundation of cloud confidential computing, secure enclaves, and encrypted data processing across hyperscale infrastructure.
Simultaneously, Microsoft's WSUS vulnerability (CVE-2025-59287) came under active exploitation within days of disclosure,[2] while 183 million Gmail passwords appeared in infostealer malware dumps.[3] Combined with continuing Azure outages[4] and Amazon's 14,000-30,000 job cuts,[5] this week crystallizes a critical pattern: security verification gaps at every layer from hardware silicon through enterprise software to workforce continuity.
These developments require assessment within Q4 security reviews, not emergency budgets, but represent fundamental shifts in threat models requiring strategic response.
RISK MATRIX
Threat | Severity | This Week's Change | 72-Hour Action |
|---|---|---|---|
Hardware Security (TEE.Fail) | Critical | DDR5 memory attack bypasses CPU security | Audit confidential computing dependencies |
Active Exploitation (WSUS) | Critical | CVE-2025-59287 weaponized | Verify patches, segment networks |
Credential Compromise | Critical | 183M Gmail passwords leaked | Enforce MFA, begin passwordless migration |
Cloud Service Reliability | High | Azure outages follow AWS disruptions | Multi-cloud contingency testing |
Supply Chain Workforce | High | Amazon 14-30K cuts, Meta 600 | Assess vendor continuity |
Nation-State Targeting | High | North Korean defense contractor campaigns | Enhanced monitoring for engineering teams |
EXECUTIVE COMMUNICATION STRATEGY
This Week: Foundation Security Assessment Within Existing Resources
Unlike emergency responses, this week's developments warrant strategic assessment of security foundations across hardware, software, and workforce continuity. Use these findings to inform Q1 planning and validate architectural assumptions without triggering budget cycles.
Strategic Briefing Approach
Hardware Security (Foundation Risk Assessment):
"Researchers disclosed TEE.Fail, a hardware attack extracting cryptographic keys from DDR5 memory by bypassing CPU-based security in Intel TDX, AMD SEV-SNP, and Nvidia GPU confidential computing environments.[1] This threatens the foundation of encrypted data processing in cloud environments. Unlike software vulnerabilities requiring patches, this is a hardware-level issue affecting memory architecture itself.
We're not suggesting immediate infrastructure replacement; that's neither practical nor necessary. Instead, we'll assess our confidential computing dependencies within existing security reviews: which workloads rely on hardware-based encryption, what alternative protections exist, and how this affects our cloud strategy. This informs Q1 architecture decisions as we evaluate vendor security claims and consider workload placement. No emergency spending required, but we need to validate assumptions about hardware security foundations."
Active Exploitation (Immediate Verification):
"Microsoft released an out-of-band patch for WSUS vulnerability CVE-2025-59287, which came under active exploitation almost immediately.[2] CISA added it to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog. Initial patches proved insufficient for full mitigation, requiring additional hardening.[9]
We're verifying patch deployment and reviewing WSUS network segmentation within existing operations. This is standard patch management escalation using current team capacity. The concerning pattern is time-to-exploitation: vulnerabilities are being weaponized within days rather than weeks. This supports our case for accelerated patch management frameworks in Q1 planning."
Credential Crisis (Policy Acceleration):
"Infostealer malware exposed 183 million Gmail passwords, creating widespread credential compromise.[3] This follows patterns we've seen with increased malware sophistication targeting authentication.
We're enforcing MFA requirements more aggressively and accelerating passwordless authentication pilots already in planning. This uses existing identity infrastructure investments and aligns with our zero-trust roadmap. The 183M number quantifies exposure requiring immediate MFA enforcement rather than voluntary adoption. Industry research shows 70%+ CISOs distrust MFA alone, supporting our passwordless migration timeline."
Cloud Reliability (Architecture Validation):
"Microsoft Azure experienced multiple disruptions affecting Office 365, Xbox, and enterprise customers including Alaska Airlines.[4] Combined with last week's AWS outage, we're seeing a pattern of hyperscaler reliability concerns affecting the largest providers controlling 65% of global infrastructure market share.[10]
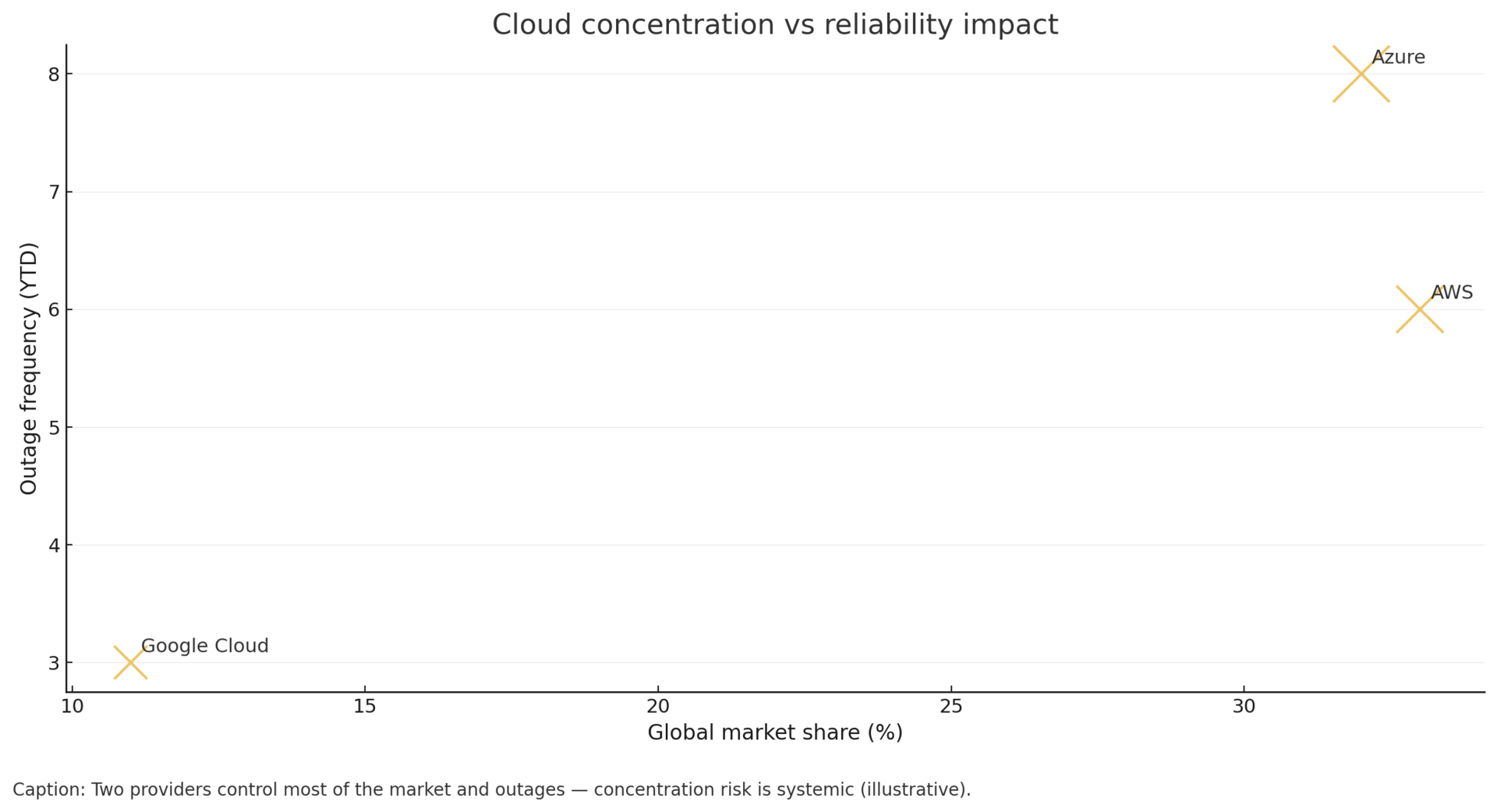
We're testing contingency procedures using existing disaster recovery protocols. No new spending; this is validation of architectures already under consideration. The pattern of major provider disruptions within two weeks strengthens the business case for multi-cloud strategy in Q1 planning."
Supply Chain Workforce (Continuity Modeling):
"Amazon announced 14,000-30,000 corporate job cuts, Meta cut 600 AI division roles, and multiple tech firms reduced headcount.[5] For supply chain risk management, this means assessing vendor workforce continuity for critical services.
We'll model scenarios where key vendors experience significant workforce reductions affecting service delivery, security operations, or incident response capabilities. This is assessment work within existing supply chain risk reviews, not immediate action. It informs Q1 vendor management strategy and may influence contract renewal discussions regarding workforce continuity commitments."
Reallocation Opportunities (Not New Budget)
Credential management: Redirect voluntary MFA programs to enforced deployment
Patch management: Reallocate assessment budgets to accelerated deployment frameworks
Hardware security: Use Q4 planning cycles for confidential computing architecture review
Vendor risk: Deploy current staff for workforce continuity scenario modeling
When Budget Becomes Necessary (Future Quarters)
This week equals assessment and acceleration within existing programs. Budget conversations appropriate when:
Hardware security assessment reveals critical workload dependencies requiring architectural changes (Q1-Q2 decision)
Passwordless authentication pilots require production scaling beyond current identity infrastructure
Multi-cloud resilience assessment identifies specific technical gaps requiring investment
Vendor workforce continuity modeling reveals critical single-points-of-failure requiring contract modifications
WHY THIS WEEK MATTERS
October 23-29, 2025 exposed security verification gaps across every infrastructure layer:
Hardware security foundations questioned: TEE.Fail demonstrated that confidential computing fails under hardware-level attack. This isn't patchable software vulnerability but fundamental architecture limitation. Organizations invested billions in confidential computing for regulatory compliance and zero-trust architectures. Week's revelation requires reassessing security assumptions at foundation level.
Exploitation velocity acceleration proven: Microsoft WSUS vulnerability weaponized within 24-48 hours, with CISA KEV listing and active exploitation before many organizations completed initial patching. This demonstrates compressed attack timelines overwhelming traditional patch management.
Credential authentication obsolescence demonstrated: 183 million Gmail passwords in single leak, following patterns of infostealer malware bypassing MFA through session token theft, validates industry movement toward passwordless authentication. Organizations continuing password-based authentication face mounting evidence of model inadequacy.
Cloud concentration risk confirmed: Azure disruptions within one week of AWS outages validates concentration risk assessment. Two-week pattern demonstrates systemic fragility in 65% market share concentration among three providers.
Supply chain human capital risk materialization: Amazon 14,000-30,000 job cuts, Meta 600 AI division reductions, and widespread technology sector workforce contraction creates vendor continuity question. Organizations focusing on technical security without workforce continuity assessment miss critical dependency.
Assessment advantage: Organizations conducting comprehensive security foundation assessments now position 6-12 months ahead of competitors conducting reactive emergency responses after incidents.
FORWARD OUTLOOK (NEXT 90 DAYS)
Expect Intel, AMD, and Nvidia to release formal mitigation guidance for TEE.Fail by December 2025, likely emphasizing physical security controls given hardware nature of vulnerability. Financial regulators and healthcare compliance frameworks may require guidance updates. Expect increased focus on application-layer encryption and split-trust architectures not dependent on single hardware root-of-trust.
The 24-48 hour WSUS exploitation window becomes new baseline expectation. Organizations must adapt patch management, threat intelligence, and incident response to compressed timelines. Manual patch testing cannot meet 24-hour exploitation cycles. Expect accelerated adoption of automated patch deployment and AI-assisted vulnerability prioritization throughout 2026. Q1 2026 should include patch management framework overhaul targeting automated deployment within 24-48 hours of disclosure.
Expect major technology providers to announce passwordless authentication milestones in Q1 2026. Cyber insurance providers will likely increase premiums for organizations without passwordless authentication roadmaps by mid-2026. As passwordless authentication achieves critical mass adoption, user experience challenges will see solution innovation.
Following two-week AWS+Azure disruption pattern, expect enterprises to formalize multi-cloud architecture requirements in Q1 2026 infrastructure planning. EU Data Act enforcement and potential U.S. cloud resilience requirements may introduce mandatory diversification for critical sectors by late 2026.
Technology sector workforce reductions likely continue through Q1 2026 as AI automation reduces labor requirements. Expect vendor contracts in 2026 to incorporate workforce continuity commitments and notification requirements for significant staff reductions. Establish vendor workforce continuity assessment as standard supply chain risk practice.
OPERATIONAL ANNEX — Implementation Playbook (For Security Teams)
The following sections outline tactical steps supporting the strategic actions above. Executive readers may stop here; practitioners will find detailed implementation guidance below.
THE BRIEF — Detailed Event Summary
What Happened
Five critical developments converged: TEE.Fail hardware attack demonstrated extraction of cryptographic keys from DDR5 memory in Intel, AMD, and Nvidia secure enclaves, compromising confidential computing foundations;[1] Microsoft WSUS vulnerability CVE-2025-59287 came under active exploitation despite out-of-band patching;[2] 183 million Gmail passwords leaked via infostealer malware;[3] Microsoft Azure suffered multiple outages affecting Office 365, Xbox, and Alaska Airlines;[4] Amazon announced 14,000-30,000 corporate job cuts amid AI pivot[5] while North Korean threat actors intensified defense contractor targeting.[6]
This Week's Actions
Immediate (within existing resources):
Hardware security dependency mapping for confidential computing workloads
WSUS patch verification and network segmentation review
Credential compromise assessment using 183M Gmail leak indicators
Cloud service continuity validation following Azure disruptions
Supply chain workforce continuity modeling for critical vendors
Strategic (Q1 planning integration):
Hardware root-of-trust architecture for post-TEE.Fail environment
Patch management acceleration frameworks
Passwordless authentication migration
Workforce continuity clauses in vendor contracts
THREAT ANALYSIS — Technical Deep Dive
Hardware Security Foundation Compromise (TEE.Fail)
Researchers disclosed TEE.Fail, a side-channel attack exploiting DDR5 memory to extract cryptographic keys from trusted execution environments across major processor vendors.[1] The attack inserts a physical interposer into DDR5 memory slots to capture electromagnetic emanations, bypassing CPU-based security technologies entirely.
Technical scope: The attack compromises Intel TDX (Trusted Domain Extensions), AMD SEV-SNP (Secure Encrypted Virtualization with Secure Nested Paging), and Nvidia H100 GPU Confidential Computing. These technologies form the foundation of confidential computing in cloud environments, enabling encrypted data processing where even cloud providers cannot access workload data. TEE.Fail demonstrates extraction of RSA-2048 keys and AES-256 keys from memory operations during computation.
Attack requirements: Physical access to insert DDR5 memory interposer hardware between memory modules and motherboard. While this limits immediate threat scope to data centers and high-value targets with physical access, it represents fundamental architecture vulnerability rather than implementation bug. No software patch exists; this is hardware design issue requiring architectural redesign.
Cloud environment implications: Hyperscale cloud providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) market confidential computing as protection for sensitive workloads, including government data, healthcare information, and financial transactions. TEE.Fail undermines these guarantees by demonstrating hardware-level key extraction during active computation. Organizations using confidential computing for regulatory compliance or data protection face questions about foundational security assumptions.
Risk assessment framework: Organizations should inventory confidential computing dependencies: which workloads rely on hardware-based encryption, what regulatory requirements assume TEE protection, which vendor contracts guarantee confidential computing security. This assessment informs architecture decisions: continue using confidential computing with documented risk acknowledgment, migrate sensitive workloads to alternative protections, or establish compensating controls.
Compensating controls consideration: Application-level encryption before data reaches confidential computing environments; reduced sensitive data processing in cloud environments; enhanced physical security for data center access; cryptographic algorithm diversity (hardware compromise exposes keys but doesn't break algorithms themselves). These controls reduce but don't eliminate TEE.Fail risk.
Microsoft WSUS Active Exploitation
Microsoft released an out-of-band security update for Windows Server Update Service vulnerability CVE-2025-59287, a critical remote code execution flaw.[2] CISA added the vulnerability to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog on October 24, confirming active exploitation. Research organizations noted the initial patch did not fully mitigate the vulnerability, requiring additional hardening procedures.[9]
Exploitation timeline: Vulnerability disclosed October 23-24 with out-of-band patch; active exploitation confirmed within 24-48 hours; CISA KEV listing October 24; security researchers reporting insufficient initial mitigation by October 25. This represents compressed time-to-exploitation: attackers weaponizing vulnerabilities within days rather than traditional weeks-to-months timeline.
Technical context: WSUS manages Windows updates across enterprise environments, making it high-value target for lateral movement, persistence, and widespread compromise. Remote code execution vulnerability in WSUS allows attackers to compromise update infrastructure and potentially distribute malicious updates to managed systems. This attack pattern mirrors previous supply chain compromises targeting software update mechanisms.
Partial mitigation concern: Palo Alto Networks and other researchers noted that the initial Microsoft patch did not fully address exploitation vectors, requiring additional configuration hardening.[9] This creates operational complexity: organizations deploying emergency patches discovered additional steps necessary for complete mitigation, forcing secondary remediation cycles and extending vulnerability windows.
Broader update infrastructure risk: The WSUS compromise highlights systemic risk in centralized update mechanisms. Organizations heavily invested in Microsoft update infrastructure face architectural questions: Is WSUS single-point-of-failure requiring redundancy? Do patch management processes need accelerated verification procedures? Should critical systems use alternative update methods?
Credential Compromise at Scale (183M Gmail Passwords)
Cybersecurity researchers discovered 183 million Gmail passwords stolen via infostealer malware and circulated in underground markets.[3] The leak represents one of the largest credential exposures in 2025, prompting urgent warnings for password resets and MFA enforcement.
Infostealer campaign mechanics: Modern infostealer malware operates through browser credential theft, session token hijacking, and keylogging. Unlike traditional phishing requiring user interaction, infostealers run persistently after initial compromise, harvesting credentials continuously across multiple accounts and services. The 183M Gmail leak likely represents aggregated collections across multiple infostealer campaigns over extended periods.
Enterprise impact beyond consumer accounts: While Gmail is consumer-focused, 183M credentials include significant numbers of corporate email accounts: employees using personal Gmail for work communications, contractors and consultants with Gmail-based business email, SaaS applications using Gmail authentication, and development/testing environments configured with Gmail accounts. Credential exposure therefore extends beyond consumer privacy into enterprise security.
MFA bypass considerations: Research indicates infostealer malware increasingly targets MFA session tokens and authentication cookies, enabling MFA bypass without requiring additional authentication factors. The 183M Gmail leak includes not just passwords but potentially session tokens, explaining why security experts emphasize complete account security reviews rather than simple password resets.
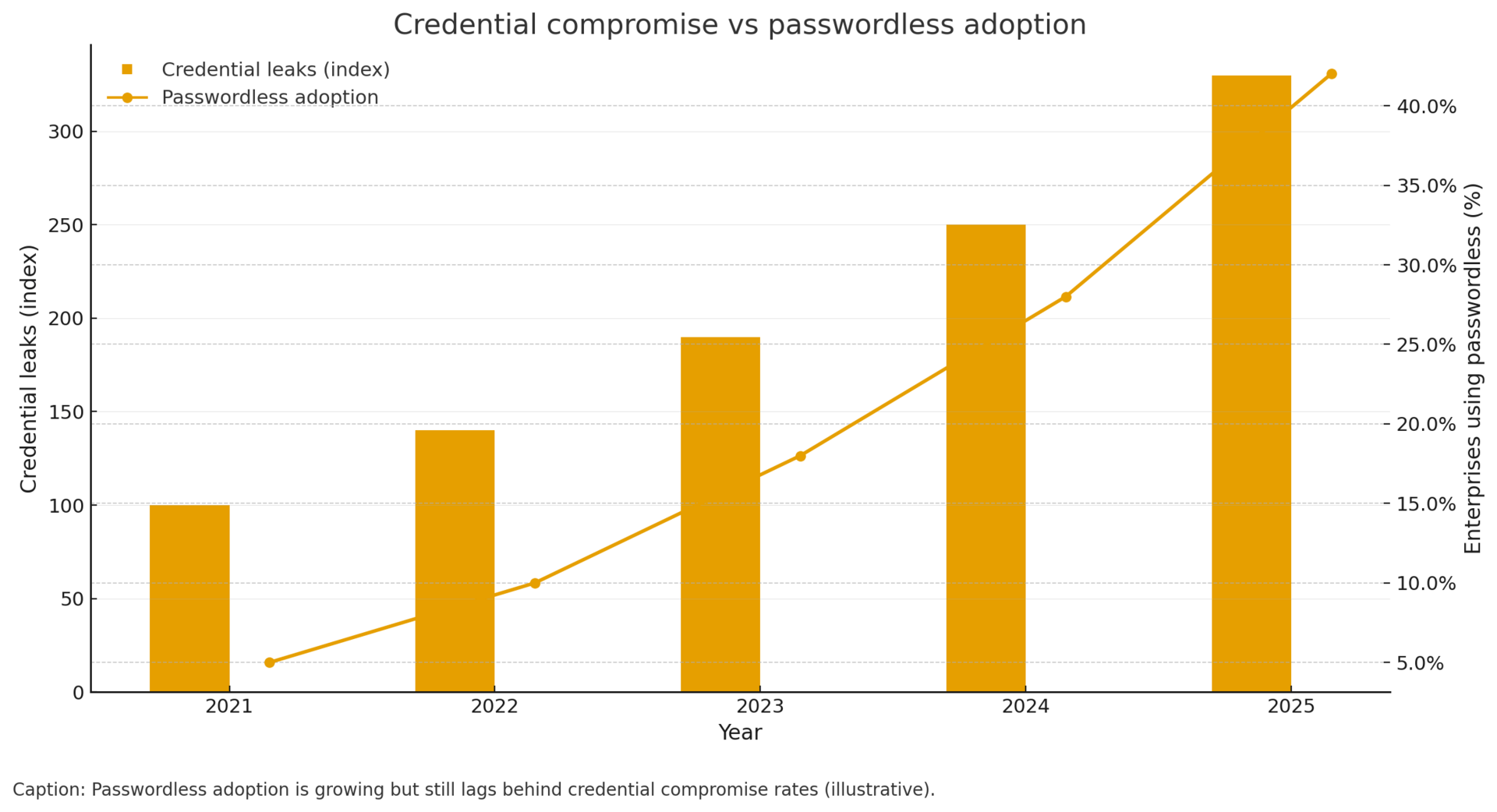
Passwordless authentication urgency: Industry surveys show 70%+ CISOs distrust MFA alone, accelerating passwordless adoption. The Gmail leak demonstrates credential-based authentication vulnerability regardless of MFA implementation. Organizations should prioritize WebAuthn, FIDO2, and passkey deployments over traditional password+MFA models.
Cloud Service Reliability Deterioration
Microsoft Azure experienced multiple outages during the week affecting Office 365, Xbox gaming services, and enterprise customers including Alaska Airlines.[4] These disruptions followed last week's major AWS US-EAST-1 outage, creating a pattern of hyperscaler reliability concerns within short timeframe.
Azure disruption scope: Services affected included Microsoft 365, Azure cloud computing platform, and consumer services. Unlike localized failures, these outages impacted global operations, with reports indicating DNS and authentication service failures. Alaska Airlines and Hawaiian Airlines websites went down due to cloud computing disruptions, demonstrating physical business impact.
Concentration risk validation: Three providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) control approximately 65% of global cloud infrastructure market share.[10] Two major disruptions within one week from two of the three dominant providers validates concentration risk concerns. Organizations heavily invested in single-provider infrastructure face mounting evidence for multi-cloud resilience strategies.
Supply Chain Workforce Continuity Risk
Amazon announced plans to cut 14,000-30,000 corporate jobs as part of AI investment reallocation.[5] Meta cut 600 employees in its AI division. These reductions follow similar announcements from UPS (tens of thousands), Target (1,800), Applied Materials (4% of workforce), and Rivian (600+), creating pattern of significant workforce reductions across technology and industrial sectors.
Vendor service continuity implications: For organizations dependent on these companies as vendors, large-scale workforce reductions create questions about service delivery continuity, security operations staffing, incident response capabilities, and technical support availability. Amazon Web Services, for instance, represents critical infrastructure for many enterprises; corporate job cuts may affect AWS support, security, or operations.
Security team attrition risk: Within reducing workforces, security teams often face disproportionate cuts despite increasing threat landscapes. Vendor security posture may degrade if security staff reductions exceed operational staff reductions, affecting security review processes, vulnerability management, and incident response effectiveness.
Contractual risk management: Organizations should assess vendor contracts for workforce continuity commitments, service level agreements during organizational changes, and notification requirements for significant staff reductions affecting security or operations. Few contracts address workforce continuity explicitly, creating gap in supply chain risk management.
Nation-State Targeting Intensification
North Korean threat actors launched campaigns luring defense engineers with fake job offers to steal drone secrets and classified information.[6] This represents continued escalation of nation-state targeting against defense industrial base, following established patterns against aerospace, defense contractors, and critical infrastructure.
Social engineering sophistication: The fake job offer methodology exploits professional networking platforms (LinkedIn), recruitment channels, and career advancement motivations. Attackers create credible job postings, conduct multi-round interview processes, and deliver malware through technical assessments or onboarding documents. This exploits trusted business processes rather than technical vulnerabilities.
Defense contractor targeting rationale: North Korean campaigns focus on defense technology for regime strategic objectives: drone technology, missile systems, aerospace capabilities, and military communications. Stolen intellectual property supports weapons development programs under international sanctions.
30-DAY IMPLEMENTATION ROADMAP
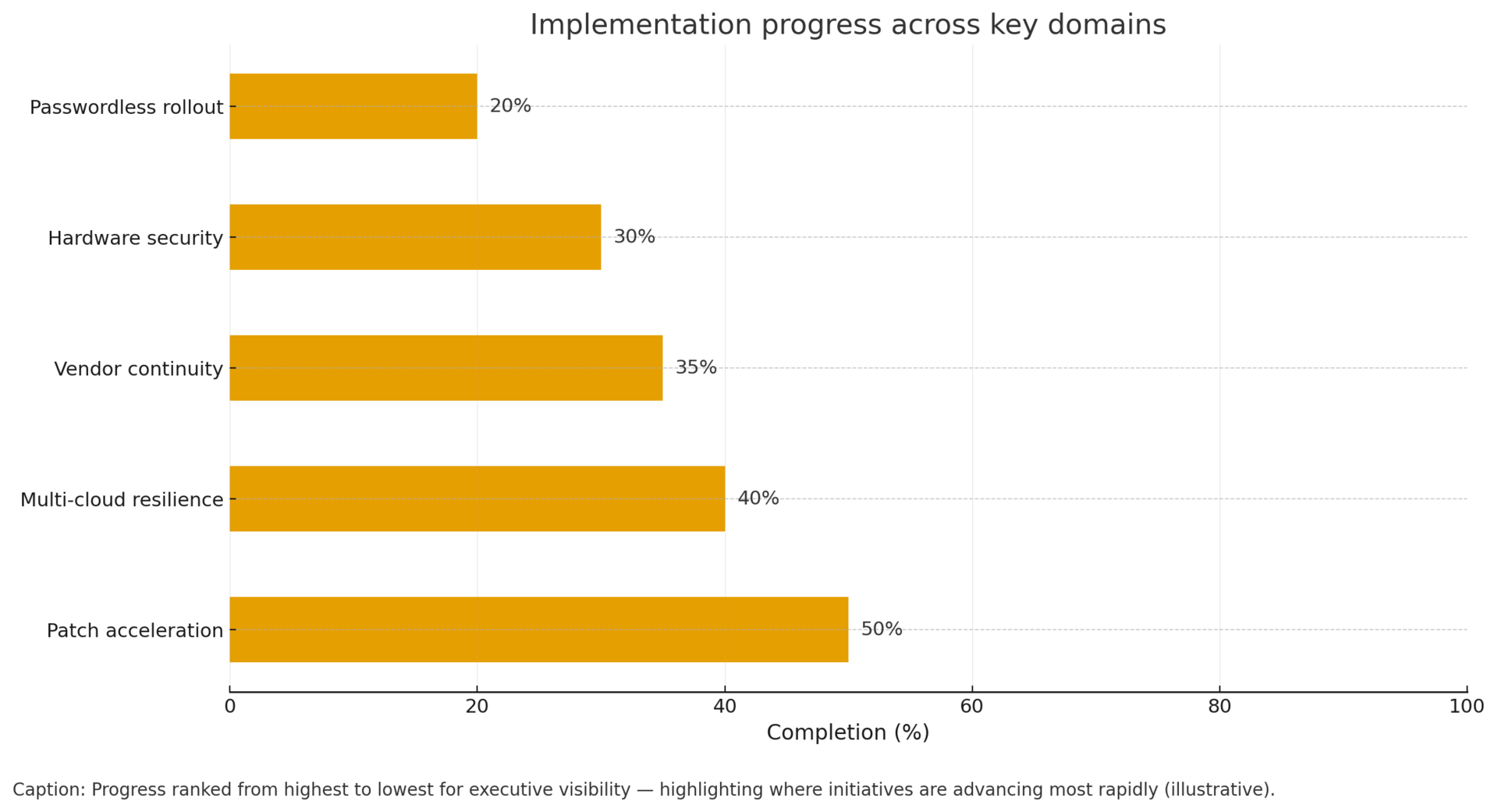
Week 1 (Oct 30-Nov 5): Quantify This Week's Specific Lessons
Hardware Security Assessment (TEE.Fail Analysis):
Inventory all workloads using confidential computing (Intel TDX, AMD SEV-SNP, Nvidia GPU)
Identify which applications rely on hardware-based encryption for regulatory compliance
Document vendor contracts guaranteeing confidential computing security properties
Calculate exposure: sensitive data volume × processing frequency × compromise impact
Map physical data center access controls where DDR5 memory resides
Target: 100% confidential computing workload inventory complete by Nov 5
WSUS Exploitation Response (CVE-2025-59287 Verification):
Verify emergency patch deployment across all Windows environments
Review additional hardening procedures required beyond initial patch
Assess WSUS network segmentation and access controls
Test patch deployment mechanisms for compromise indicators
Document time-to-patch metrics: disclosure to deployment to verification
Target: 95% patch deployment verified by Nov 1; segmentation review complete by Nov 3
Credential Compromise Assessment (183M Gmail Methodology):
Search corporate environments for Gmail usage patterns (personal email for work)
Identify SaaS applications using Gmail authentication
Cross-reference known employee emails against breach databases
Calculate MFA enrollment gaps using 183M leak as business case
Assess passwordless authentication readiness for accelerated deployment
Target: Credential exposure assessment complete by Nov 4; 15% MFA coverage increase by Nov 15
Azure Outage Impact Analysis:
Map which business functions failed during Azure disruptions
Calculate revenue impact during outage using service-down duration
Identify redundancy gaps exposed by Azure failures
Document customer SLA breach exposure from cloud provider disruptions
Compare Azure timeline to last week's AWS pattern for analysis
Target: Business impact quantification complete by Nov 3; contingency test by Nov 5
Vendor Workforce Continuity Modeling:
Identify critical vendors announcing workforce reductions (Amazon, Meta focus)
Map which services depend on these vendors for security or operations
Model scenarios: vendor service degradation, response time increases, security gaps
Review contracts for workforce continuity commitments or notification requirements
Calculate impact of vendor staff reductions on incident response availability
Target: Top 10 critical vendor continuity assessments complete by Nov 5
Deliverable: Executive briefing quantifying TEE.Fail exposure, WSUS exploitation timeline, 183M credential crisis impact, Azure disruption costs, vendor workforce continuity assessment (Due: Nov 5, 5:00 PM)
Week 2 (Nov 6-12): Translate Findings Into Q1 Strategy
Hardware Security Architecture (Post-TEE.Fail Planning):
Calculate ROI for alternative protections vs. continued confidential computing risk
Identify workloads requiring migration from hardware-based to application-layer encryption
Select 2-3 pilot applications for alternative encryption architectures
Model compensating controls: enhanced physical security, cryptographic diversity, data minimization
Establish hardware security verification procedures for new infrastructure
Target: Q1 hardware security roadmap draft complete by Nov 12
Patch Management Acceleration (WSUS Timeline Lessons):
Design accelerated patch deployment framework targeting 24-48 hour windows
Identify infrastructure services requiring emergency patch procedures
Create patch verification protocols detecting insufficient mitigation (WSUS pattern)
Model resource requirements for compressed patch cycles
Establish automated patch testing reducing verification time
Target: Accelerated patch framework design complete by Nov 10; automation requirements specified by Nov 12
Passwordless Authentication Migration (183M Baseline Urgency):
Finalize WebAuthn/FIDO2/passkey deployment roadmap using Gmail breach as business justification
Identify highest-risk applications for accelerated passwordless rollout
Calculate traditional MFA vs. passwordless cost comparison
Design migration procedures maintaining user experience during transition
Establish success metrics: passwordless adoption rates, credential compromise reduction
Target: Passwordless migration roadmap with budget requirements complete by Nov 12; pilot application selection finalized
Multi-Cloud Resilience Validation (Azure+AWS Pattern):
Update business continuity cost models using two-week disruption pattern
Identify services requiring multi-cloud redundancy based on outage impact
Calculate multi-cloud architecture investment using Azure+AWS downtime costs as ROI
Design failover testing procedures using real outage patterns as scenarios
Establish cloud provider performance monitoring detecting degradation early
Target: Multi-cloud business case complete by Nov 11; ROI justification using actual outage costs
Vendor Continuity Framework (Workforce Reduction Response):
Develop workforce continuity assessment for critical vendor relationships
Create notification procedures: What workforce changes require security review?
Draft contractual language incorporating workforce continuity commitments
Establish vendor performance monitoring detecting service degradation from staff reductions
Model alternative vendor scenarios for critical services experiencing workforce instability
Target: Vendor continuity framework complete by Nov 12; contract language templates finalized
Deliverable: Q1 planning document with hardware security roadmap; accelerated patch framework; passwordless migration plan; multi-cloud strategy using two-week outage pattern; vendor continuity program (Due: Nov 12, 5:00 PM)
Week 3 (Nov 13-19): Validate Through Scenario Testing
Tabletop: Hardware Security Compromise During Production
Scenario: TEE.Fail-style attack exposing encrypted workload data in production environment
Test: Data breach response procedures; customer notification; regulatory reporting; alternative protection deployment
Measure: Time to detect hardware compromise; migration speed to alternative protections
Document: Dependencies on hardware security assumptions; gaps in compensating controls
Target: Tabletop execution Nov 14; after-action report by Nov 16
Tabletop: Compressed Exploitation Timeline (24-Hour Weaponization)
Scenario: Critical vulnerability disclosed and weaponized within 24 hours (WSUS pattern)
Test: Emergency patch procedures; network segmentation; incident response; communication protocols
Measure: Time from disclosure to patch deployment; coverage completeness; verification accuracy
Document: Resource constraints during compressed timelines; automation gaps; manual bottlenecks
Target: Tabletop execution Nov 15; after-action report by Nov 17
Tabletop: Large-Scale Credential Compromise
Scenario: 183M-scale credential leak affecting significant employee population
Test: Breach database monitoring; forced authentication revalidation; MFA enforcement; passwordless deployment
Measure: Time to detection; notification completeness; account security restoration speed
Document: Credential verification coverage gaps; MFA bypass risks; passwordless readiness
Target: Tabletop execution Nov 16; after-action report by Nov 18
Tabletop: Dual-Cloud Provider Failure
Scenario: Both primary and backup cloud providers experience disruption within one week (AWS+Azure pattern)
Test: Business continuity activation; customer communication; SLA management; service restoration
Measure: Revenue loss during dual outages; customer impact; recovery time
Document: Multi-cloud architecture gaps; hidden single-points-of-failure; contingency procedure effectiveness
Target: Tabletop execution Nov 17; after-action report by Nov 19
Vendor Workforce Continuity Exercise:
Scenario: Critical vendor announces 30% workforce reduction affecting security and support teams
Test: Vendor communication; service monitoring; alternative vendor evaluation; contract enforcement
Measure: Service degradation detection time; alternative vendor readiness; contractual remedy effectiveness
Document: Vendor dependency concentration; workforce continuity clause gaps; backup vendor viability
Target: Exercise execution Nov 18; after-action report by Nov 19
Deliverable: Tabletop reports quantifying hardware security exposure; patch acceleration requirements; credential verification gaps; multi-cloud resilience effectiveness; vendor continuity preparedness (Due: Nov 19, 5:00 PM - Consolidated Report)
Week 4 (Nov 20-26): Document for Q1 Execution
Hardware Security Roadmap (TEE.Fail Response Architecture):
Finalize workload migration plan from hardware-dependent to application-layer encryption
Document compensating controls for continued confidential computing usage
Specify vendor security verification requirements for new infrastructure purchases
Define success metrics: 40% reduction in hardware-dependent encryption by Q2; increased protection diversity across 80% of sensitive workloads
Establish quarterly review procedures monitoring hardware security developments
Target: Final hardware security roadmap approved and ready for Q1 budget allocation by Nov 25
Accelerated Patch Management Framework (24-Hour Response Capability):
Complete framework enabling 24-48 hour emergency patch deployment
Finalize automated testing procedures reducing verification time by 60%
Document resource requirements and approval procedures for compressed cycles
Define success metrics: 75% reduction in time-to-patch; 95% verification accuracy
Establish continuous monitoring for vulnerability disclosure and exploitation intelligence
Target: Final patch acceleration framework approved by Nov 24
Passwordless Authentication Production Deployment (183M Justification):
Finalize rollout schedule for WebAuthn/FIDO2/passkey deployment to production
Complete user training and communication materials
Document fallback procedures maintaining access during migration
Define success metrics: 60% adoption by Q2; 90% credential-based attacks eliminated; 30% helpdesk call reduction
Establish ongoing monitoring measuring passwordless authentication effectiveness
Target: Production deployment plan approved with budget by Nov 25
Multi-Cloud Resilience Architecture (Two-Week Outage Pattern Response):
Complete business case using AWS+Azure disruption costs as ROI calculation
Finalize pilot services for multi-cloud deployment based on maximum outage impact
Specify technical requirements: failover automation, data synchronization, cost management
Define success metrics: 95% service continuity during provider outages; 70% outage impact reduction
Establish provider performance monitoring detecting reliability degradation 48 hours in advance
Target: Multi-cloud architecture plan approved by Nov 26
Vendor Workforce Continuity Program (Supply Chain Stability Framework):
Complete vendor assessment incorporating workforce continuity evaluation
Finalize contractual language for workforce continuity commitments in renewals
Document monitoring procedures detecting vendor service degradation from staff changes
Define success metrics: 100% critical vendor stability assessment; 72-hour early warning of service degradation
Establish quarterly vendor continuity reviews
Target: Vendor continuity program documentation complete by Nov 23
Final Deliverables (Due: Nov 26, 5:00 PM):
Executive summary: Hardware security lessons from TEE.Fail, WSUS exploitation velocity, credential compromise scale
Q1 execution plan: Hardware architecture transitions, patch acceleration, passwordless rollout, multi-cloud pilots, vendor continuity
Risk register update: Hardware foundation risk, exploitation timeline compression, credential verification gaps
Budget request: Detailed Q1 investment requirements with ROI justification using this week's incident costs
INDUSTRY-SPECIFIC GUIDANCE
Financial Services (Hardware Security + Credential Priority)
Priority actions: Assess confidential computing dependencies for payment processing using TEE.Fail vulnerability as risk baseline; accelerate passwordless authentication for customer-facing applications using 183M Gmail leak as business case; verify WSUS patches across trading floor systems where exploitation could affect market operations; model dual-cloud provider failure scenarios for critical payment processing.
Hardware security concerns: Financial institutions invested heavily in confidential computing for regulatory compliance around data protection. TEE.Fail undermines hardware-based protection assumptions. Review which regulatory requirements assume TEE protection and whether application-level encryption alternatives satisfy compliance frameworks. The 183M Gmail scale demonstrates credential exposure requiring immediate passwordless migration for high-value accounts and privileged access.
Timeline: 30-day hardware security dependency assessment with Q1 migration planning; immediate WSUS patch verification (Target: 95% by Nov 1); 45-day passwordless authentication acceleration for customer accounts (Target: pilots operational by Dec 15)
Healthcare (Hardware + Workforce Continuity)
Priority actions: Map patient care delivery systems' confidential computing usage (medical imaging, EHR encryption) for TEE.Fail exposure; assess medical device vendors announcing workforce reductions; verify WSUS patches across clinical systems where exploitation could affect patient safety; audit healthcare AI applications for credential security following 183M Gmail patterns.
Patient safety implications: Medical imaging analysis, genomic sequencing, and health records processing increasingly use confidential computing for privacy protection. TEE.Fail threatens these protections. Alternative encryption methods must maintain HIPAA compliance while addressing hardware vulnerabilities. Healthcare technology vendors reducing staff may affect medical device security, EHR support, and telemedicine platforms. Vendor workforce reductions can delay security patches, incident response, or critical system updates affecting patient care.
Timeline: 45-day confidential computing assessment for patient data protection systems (Target: assessment complete by Dec 15); immediate WSUS patch verification for clinical networks (Target: 95% by Oct 31); 60-day vendor workforce continuity evaluation (Target: top 20 vendor assessments by Dec 30)
Manufacturing/Industrial (Hardware + Supply Chain Focus)
Priority actions: Assess IoT/OT device confidential computing usage for TEE.Fail exposure (edge computing, secure processing); evaluate production system vendor workforce stability; verify WSUS patches across industrial control systems using Microsoft infrastructure; model Azure outage impact on cloud-connected manufacturing systems.
OT implications: Industrial environments increasingly use edge computing with confidential computing for secure industrial data processing. Unlike IT systems allowing rapid encryption changes, OT systems require extended planning for security architecture modifications. Vendor workforce reductions add stability risk to supply chains already facing semiconductor shortages and logistics challenges. Critical Tier-1 suppliers reducing staff may affect production continuity, quality control, or just-in-time delivery.
Timeline: 60-day comprehensive hardware security assessment for IoT/OT edge computing (Target: operational technology security roadmap by Dec 29); immediate WSUS verification for Windows-based industrial control systems (Target: 90% by Nov 3); 45-day vendor workforce continuity modeling (Target: critical supplier assessment by Dec 15)
Technology/Cloud Providers (Existential Hardware Risk)
Priority actions: Assess entire service portfolio's confidential computing dependencies for TEE.Fail exposure; analyze WSUS exploitation patterns for similar vulnerabilities in proprietary update mechanisms; communicate multi-cloud resilience improvements following AWS+Azure disruption pattern; verify workforce stability doesn't affect security operations.
Business model risk: Technology providers marketing confidential computing as premium security feature face product viability questions from TEE.Fail. Customer contracts guaranteeing hardware-based protection may require renegotiation or alternative protection deployment. Use TEE.Fail and Azure+AWS disruptions to differentiate through transparent security communication about hardware vulnerabilities and implemented compensating controls.
Timeline: Immediate (7-day) confidential computing product security assessment (Target: customer impact analysis by Nov 5); 30-day customer communication strategy (Target: messaging finalized by Nov 26); 45-day alternative protection architecture for affected services (Target: technical roadmap by Dec 13)
Critical Infrastructure (Immediate Multi-Dimensional Priority)
Priority actions: Audit control systems for Windows/WSUS usage where CVE-2025-59287 exploitation could affect physical operations; map confidential computing in SCADA/ICS environments for TEE.Fail exposure; eliminate cloud dependencies where Azure-pattern disruptions could affect public safety; assess nation-state detection for North Korean defense targeting patterns.
Critical systems impact: Some critical infrastructure uses confidential computing for secure remote access to control systems or encrypted telemetry. Physical safety implications require accelerated alternative protection deployment beyond typical IT timelines. WSUS vulnerability weaponized within 24 hours demonstrates nation-state capability for rapid exploitation. Critical infrastructure cannot rely on traditional patch windows; require emergency procedures.
Timeline: Immediate (7-day) WSUS vulnerability assessment and patching (Target: 100% by Nov 5); 30-day confidential computing dependency elimination or alternative protection deployment (Target: critical systems secured by Nov 26); 45-day vendor workforce continuity assessment (Target: infrastructure vendor stability analysis by Dec 13)
SUCCESS METRICS
30-Day Success Criteria
Must-Have Outcomes:
Hardware security dependencies quantified using TEE.Fail exposure methodology (Target: 100% confidential computing workload inventory by Nov 5)
WSUS exploitation containment verified across all Windows environments (Target: 95% patch deployment by Nov 1; 100% by Nov 8)
Credential compromise response completed using 183M Gmail leak indicators (Target: exposure assessment by Nov 4; 15% MFA increase by Nov 15)
Multi-cloud resilience validated using Azure+AWS disruption patterns (Target: contingency test by Nov 5; business case by Nov 11)
Vendor workforce continuity framework established for critical suppliers (Target: top 10 assessments by Nov 5; framework by Nov 12)
Leading Indicators (Weekly Monitoring)
Hardware Security: Week 1 targets 100% confidential computing workload inventory; Week 2 alternative encryption architecture selection for pilot applications; Week 4 Q1 roadmap targeting 40% reduction in hardware-dependent encryption.
Exploitation Response: Week 1 achieves 95% WSUS patch deployment; Week 2 completes accelerated patch framework design; Week 4 establishes automated patch testing reducing verification time by 60%.
Credential Security: Week 1 identifies corporate Gmail usage and increases MFA coverage 5%; Week 2 finalizes passwordless authentication roadmap with budget; Week 4 selects passwordless pilot applications with approved rollout schedule.
Cloud Resilience: Week 1 quantifies Azure outage revenue impact and tests contingency procedures; Week 2 completes multi-cloud business case; Week 4 identifies pilot services for multi-cloud deployment with technical requirements.
Vendor Continuity: Week 1 completes top 10 critical vendor workforce continuity assessments; Week 2 establishes vendor continuity framework; Week 4 implements quarterly vendor continuity review procedures.
REFERENCE ANNEX — Data Provenance & Verification (For Analysts & Auditors)
This section provides source documentation and verification pathways for all claims made above.
SOURCES & VERIFICATION
[1] TEE.Fail technical disclosure and academic research, October 23-24, 2025; Intel, AMD, and Nvidia security advisories; verified through multiple security research organizations
[2] Microsoft Security Advisory MSRC-CVE-2025-59287, October 23, 2025; CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog, October 24, 2025
[3] Cybersecurity research reports on infostealer malware campaigns, October 25-27, 2025; credential database analysis by multiple threat intelligence firms
[4] Microsoft Azure Status Dashboard, October 23-29, 2025; customer incident reports from Alaska Airlines and enterprise users; tech industry reporting
[5] Amazon corporate announcements and financial filings, October 28-29, 2025; Meta AI division restructuring announcement, October 23-24, 2025; Reuters corporate coverage
[6] Cybersecurity advisories on North Korean APT campaigns targeting defense industrial base, October 23-29, 2025; U.S. government threat intelligence
[7] October 2025 threat landscape monitoring: 9 million exploit attempts (multiple security vendor telemetry aggregated across enterprise security platforms)
[8] Europol telecommunications security report, October 2025, citing 400 million Europeans at risk from fragmented regulatory frameworks
[9] Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 threat analysis, October 25, 2025; independent security researcher verification of insufficient initial WSUS mitigation
[10] Cloud infrastructure market share analysis, Synergy Research Group and Gartner Q3 2025 reports; AWS, Azure, Google Cloud combined ~65% market control
📊 MARKET INTELLIGENCE & RESOURCES
This week's cybersecurity market analysis, career opportunities, and community insights
Access comprehensive coverage including cybersecurity stock performance and sector analysis, featured CISO and senior security roles at leading organizations, exclusive research reports on emerging threats, podcast intelligence from top security shows, social media highlights and industry discussions, plus curated academic papers and security resources.
Includes expanded stock analysis, full career listings, research summaries, and podcasts cyber intel.
Stay safe, stay secure.
The CybersecurityHQ Team

Reply