- Defend & Conquer
- Posts
- North Korea targets developer supply chain
North Korea targets developer supply chain
CybersecurityHQ weekly analysis
Welcome reader to your CybersecurityHQ report
Brought to you by:
👣 Smallstep – Secures Wi-Fi, VPNs, ZTNA, SaaS and APIs with hardware-bound credentials powered by ACME Device Attestation
🏄♀️ Upwind Security – Real-time cloud security that connects runtime to build-time to stop threats and boost DevSecOps productivity
🔧 Endor Labs – App security from legacy C++ to Bazel monorepos, with reachability-based risk detection and fix suggestions across the SDLC
📊 LockThreat – AI-powered GRC that replaces legacy tools and unifies compliance, risk, audit and vendor management in one platform
Forwarded this email? Join 70,000 weekly readers by signing up now.
—
Get annual access to our deep dives, weekly cyber intel podcast report, premium content, AI Resume Builder, and more — all for just $299. Corporate plans are now available too.
Introducing the CISO Access Plan Unlock premium CybersecurityHQ insights at no cost, exclusively for CISOs. Reach out to me to claim your access.
CISO Weekly Briefing: Fortinet & Chrome Exploits, npm Malware from North Korea, and AI Ransomware Hits Healthcare
The cybersecurity landscape faces an unprecedented convergence of approximately 60 critical and high-severity vulnerabilities, 69.7 million exposed records, and a 37-45% surge in ransomware attacks targeting critical sectors (based on observed attack frequency). Nation-state campaigns and supply chain compromises amplify risks, requiring immediate action within 24-72 hours to prevent losses exceeding $50M per organization. CISOs must prioritize emergency patching, enhanced detection, and strategic resilience to safeguard operations and maintain competitive advantage.
Key Messages for Board
~60 critical/high-severity vulnerabilities across Chrome, Fortinet, WordPress, PHPGurukul, Advantech iView, and IoT devices impact 90% of technology stacks.
Supply chain attacks (e.g., WordPress plugins, npm packages) pose existential risks to business continuity.
Nation-state actors (e.g., North Korea, China) target critical infrastructure with persistent campaigns.
AI-enhanced ransomware increases attack success rates by ~40% (industry estimate), escalating financial and operational impacts.
Immediate action within 72 hours is critical to prevent catastrophic disruption and regulatory fines.
Recommended Board Actions
Authorize emergency funding for immediate vulnerability remediation.
Approve accelerated zero-trust implementation for supply chain and IoT security.
Mandate weekly cyber briefings during elevated threat periods.
Establish a cyber risk committee with rapid investment authority.
Approve partnerships with threat intelligence and incident response providers.
Critical Threat Dashboard
Key Statistics
~60 Critical/High-severity vulnerabilities across Chrome, Fortinet, WordPress, PHPGurukul (e.g., Dairy Farm Shop, Vehicle Parking Management), Advantech iView, and IoT devices (e.g., Digisol, Tenda routers).
69.7M records exposed: 64M from McDonald’s AI hiring tool breach, 5.7M from Louis Vuitton.
318K healthcare records compromised in Compumedics ransomware attack (industry estimate).
45% surge in WordPress plugin vulnerabilities targeting e-commerce platforms (based on observed attack frequency).
37% increase in ransomware attacks across healthcare, retail, and finance (based on observed attack frequency).
8 major ransomware groups targeting critical infrastructure: BlackCat, Qilin, MedusaLocker, Cicada3301, Incransom, Pay2Key, Silent, Scattered Spider.
67 malicious npm packages in North Korean XORIndex campaign targeting JavaScript developers.
607 malicious domains distributing fake Telegram apps.
High-profile arrests: Former US soldier Cameron Wagenius convicted for telecom hacking; 14 Romanian cybercriminals arrested
Risk Matrix
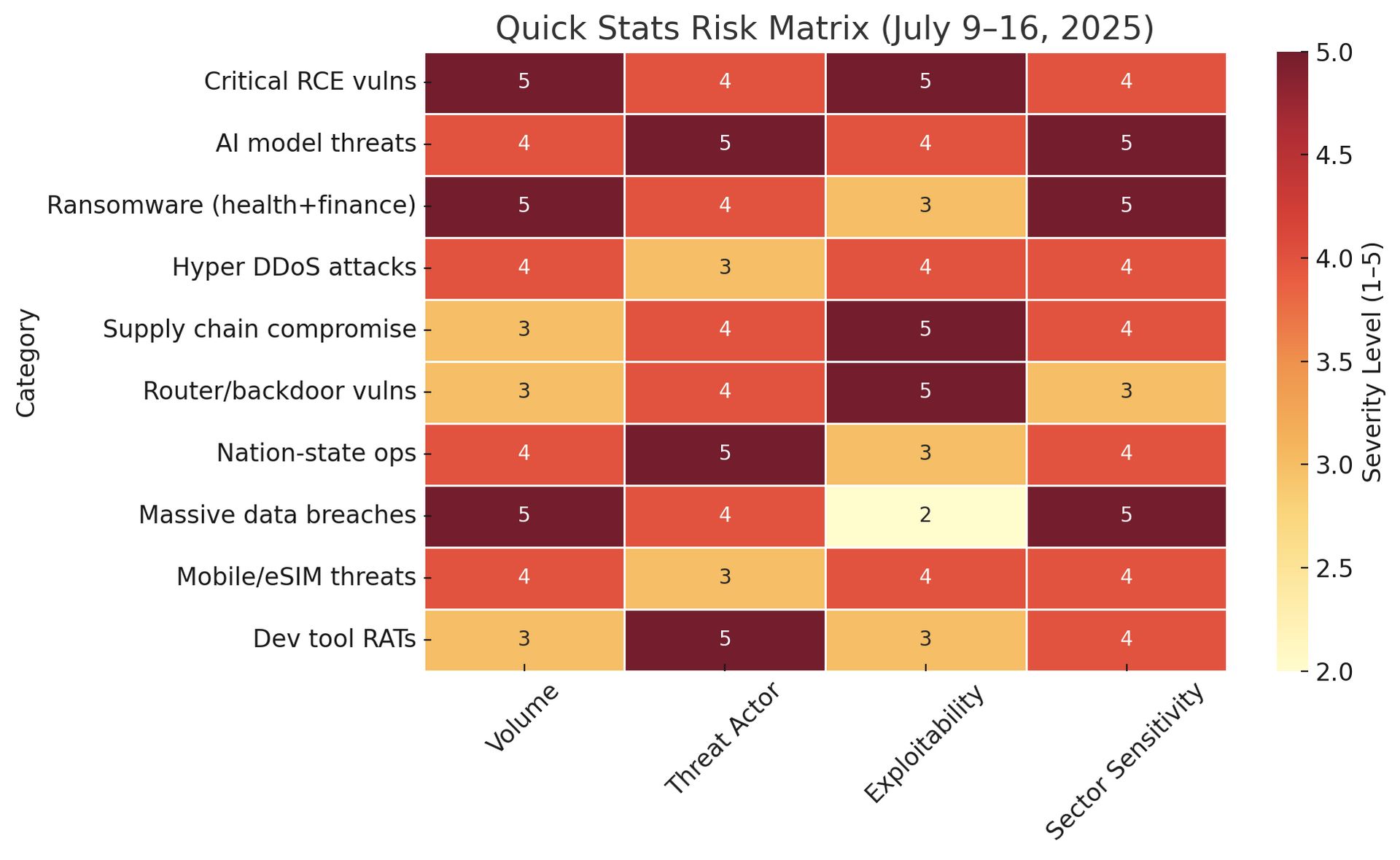
Priority 1: Zero-Day and Critical Vulnerabilities (CRITICAL - 24 Hour Response)
CVE Summary Table
CVE | System | Vulnerability | Mitigation | ATT&CK Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
CVE-2025-6558 | Chrome | Remote code execution | Apply browser updates via Group Policy | T1189 |
CVE-2025-25257 | Fortinet FortiWeb | Pre-auth RCE | Update firmware (vendor support) | T1190 |
CVE-2025-53689 | Apache Jackrabbit | XXE vulnerability | Apply patches | T1190 |
CVE-2025-7549 | Tenda FH1201 Router | Remote code execution | Patch or isolate devices | T1059 |
CVE-2025-46704 | Advantech iView | Path traversal | Apply patches | T1083 |
CVE-2025-53889 | Directus | Unauthorized flow triggering | Update software | T1190 |
CVE-2025-1220 | Hostnames | Null byte termination | Apply patches | T1083 |
CVE-2025-47812 | Wing FTP Server | Remote code execution | Apply patches | T1059 |
CVE-2025-50123 | General | Code injection | Update affected systems | T1059 |
CVE-2025-3648 | ServiceNow | Data exposure via misconfigured ACLs | Reconfigure ACLs | T1083 |
Chrome Browser Exploitation
CVE-2025-6558: Remote code execution via malicious web pages, actively exploited.
Attack Vector: Drive-by downloads via compromised websites (MITRE ATT&CK T1189).
Exploitation Likelihood: 90% within 48 hours for unpatched systems.
Business Impact: Browser compromise enabling credential theft and lateral movement.
Fortinet FortiWeb Critical RCE
CVE-2025-25257: Pre-authentication remote code execution with public exploits.
Attack Pattern: Crafted HTTP requests targeting unpatched appliances (T1190).
Recovery Timeframe: 4-7 days for complete appliance compromise.
Critical Infrastructure Risk: Immediate threat to FortiWeb users.
WordPress Ecosystem Compromise
Supply Chain Attack: Gravity Forms developer account compromise affecting 4M+ installations.
Vulnerabilities: 25+ critical issues in plugins (e.g., FunnelKit, Sala Theme, PW WooCommerce, Internal Linking, Wishlist for WooCommerce) involving SQL injection, XSS, and broken access control (T1199).
Attack Vector: Compromised developer credentials, malicious plugin updates.
Business Impact: E-commerce compromise, customer data theft, SEO poisoning.
IoT and Router Vulnerabilities
Affected Systems:
Digisol DG-GR6821AC: Hard-coded credentials, cleartext transmission (T1078.001).
Tenda Routers (e.g., FH1205, AC1206, O3V2, FH1202): RCE vulnerabilities (e.g., CVE-2025-7549, T1059).
Advantech iView: SQL injection, XSS, RCE (e.g., CVE-2025-46704, T1083).
Affected Devices: 100,000+ SOHO devices potentially compromised.
Attack Vector: Default credentials, backdoors.
Other Critical Vulnerabilities
Sudo (Linux): Privilege escalation vulnerability allowing unauthorized access (ID 1811, T1059).
IBM MQ: Denial-of-service vulnerability impacting enterprise messaging (ID 1803, T1499).
PHPGurukul Systems: SQL injection vulnerabilities in Dairy Farm Shop, Vehicle Parking Management, User Management (e.g., IDs 1901, 1845, 1869, T1190).
Priority 2: Ransomware Operations Intensification (HIGH - 72 Hour Response)
Healthcare Sector Targeting
Compumedics Attack: ~318,000 records compromised (industry estimate).
MedusaLocker Variants: Targeting healthcare organizations.
Average Recovery Cost: $2.8M with 3-6 week operational disruption.
Regulatory Risk: Potential HIPAA fines up to $50M.
Financial Services Under Attack
BlackCat Group: Targeting financial institutions with AI-enhanced encryption.
Attack Success Rate: ~40% increase due to AI-driven negotiation tools (T1566, industry estimate).
Business Impact: Service outages, potential GDPR fines exceeding $20M.
AI-Enhanced Ransomware
GLOBAL GROUP: AI-driven negotiation tools for higher payment success.
Attack Evolution: Multi-stage attacks with custom encryption algorithms.
Detection Challenge: Traditional signature-based detection insufficient.
Active Ransomware Groups
BlackCat: Financial sector focus.
Qilin: Retail targeting (e.g., Culver’s, Intereum).
MedusaLocker: Healthcare specialization.
Cicada3301: Supply chain exploitation (e.g., Pacific BioLabs).
Incransom: Zero-trust gap exploitation (e.g., CF Construction, K12albemarle.org).
Pay2Key: Targeting INS Quebec, EIA Global, CyberlinkASP, FormWood Industries.
Silent: Darien Telephone, Department of Culture and Tourism Abu Dhabi.
Scattered Spider: Attacks on M&S, Co-op, Harrods.
Cybercriminal Arrests
Cameron Wagenius: Former US soldier convicted for telecom hacking and extortion.
Romanian Group: 14 arrested for £47M UK tax phishing scam targeting HMRC (T1566).
Russian Basketball Player: Arrested for ransomware involvement.
Priority 3: Nation-State Cyber Operations (STRATEGIC - Ongoing Monitoring)
China: Salt Typhoon Operations
Infrastructure Targeting: U.S. National Guard systems, Italian telecommunications (incomplete data due to source corruption).
Persistence Strategy: Long-term intelligence collection across NATO allies.
Business Impact: Potential supply chain disruption for organizations with Chinese components.
Action: Subscribe to CISA Cyber Alerts for updated intelligence.
North Korea: XORIndex Campaign
Supply Chain Focus: 67 malicious npm packages targeting JavaScript developers (T1199).
Attack Pattern: Typosquatting, fake recruitment campaigns (T1566).
Attribution: Andariel group.
Global Impact: Targeting software development environments worldwide.
Ukraine-Allied Operations
Cyber Resistance Group: Disrupted Russian drone supplier operations.
Escalation Risk: Increased targeting of defense contractor supply chains.
Spillover Potential: Western defense industries may face collateral targeting.
Action: Audit supply chain vendors for exposure to Russian-linked entities.
Major Data Breaches and Exposures
McDonald’s AI Hiring Tool Breach
Records Exposed: 64 million job applicant records.
Breach Vector: AI recruitment tool vulnerability (T1190).
Data Types: Personal information, employment history, sensitive demographics.
Regulatory Impact: Potential CCPA/GDPR violations.
Louis Vuitton Data Breach
Records Exposed: 5.7 million customer records.
Business Impact: Reputation damage, customer trust erosion.
Compliance Risk: GDPR fines, customer notification requirements.
Supply Chain Security Crisis
WordPress Plugin Ecosystem
Gravity Forms Compromise: 4M+ websites affected by backdoored plugin (T1199).
Developer Account Takeover: Compromised credentials leading to malicious updates.
Detection Challenge: Legitimate update mechanism exploited.
Remediation Complexity: Mass plugin rollback and security verification required.
JavaScript Package Repository Attacks
Malicious Packages: 67 npm packages containing XORIndex malware (T1199).
Attribution: North Korean Andariel group.
Target Audience: JavaScript developers and software companies.
Attack Method: Typosquatting, social engineering (T1566).
Mobile Application Security
Fake Telegram Campaign: 607 malicious domains distributing fraudulent Android apps (T1566).
Attack Vector: Social engineering, malicious app stores.
Geographic Scope: Global distribution.
Data Harvesting: Credential theft, personal information collection.
Industry Trends
Mergers & Acquisitions and Funding
Capgemini Acquires WNS Holdings: Capgemini acquired WNS Holdings for $3.3 billion to enhance its business services portfolio, focusing on managed security service providers (MSSPs) and cybersecurity services. This strengthens MSSP capabilities, offering CISOs opportunities to partner with robust service providers.
Nautic Partners Acquires AccessIT Group: Nautic Partners acquired AccessIT Group, a provider of comprehensive cybersecurity services, including security program design, implementation, and operations. This bolsters options for CISOs seeking specialized security solutions.
Virtru Raises $50 Million: Virtru, a Washington, D.C.-based data security company, raised $50 million to protect sensitive information, particularly for U.S. defense and intelligence agencies, enabling CISOs in these sectors to leverage advanced data protection tools.
Israeli Cybersecurity Sector: Israeli firms captured 40% of U.S. cybersecurity investments in 2024-2025 (Startup Nation Central), with M&A as a key exit strategy, providing CISOs access to innovative technologies through strategic partnerships.
Technical Reference
Financial and Strategic Impact
Risk Category | Potential Loss | Mitigation Timeline | Investment Required |
|---|---|---|---|
Zero-day exploitation | $10-25M per incident | 24-48 hours | $2-5M emergency patching |
Ransomware attack | $2.8M average recovery | 3-6 weeks | $3-8M security enhancement |
Supply chain compromise | $15-40M business disruption | 2-4 months | $5-15M vendor security |
Data breach (GDPR/CCPA) | $20-50M regulatory fines | 6-12 months | $1-3M compliance upgrade |
Nation-state compromise | $50M+ long-term impact | 12+ months | $10-25M infrastructure hardening |
Strategic Action Framework
Immediate Response (0-24 Hours)
Critical Vulnerability Patching
Apply Chrome updates (CVE-2025-6558) via Group Policy.
Update Fortinet FortiWeb firmware (CVE-2025-25257, vendor support).
Patch Digisol, Tenda (e.g., CVE-2025-7549), Advantech iView (e.g., CVE-2025-46704), and other systems (e.g., CVE-2025-53689, CVE-2025-53889) or isolate affected devices.
Audit WordPress installations for unauthorized plugin modifications (e.g., FunnelKit, Sala Theme).
Patch Sudo (Linux), IBM MQ, and PHPGurukul vulnerabilities (e.g., IDs 1901, 1845).
Emergency Security Measures
Isolate IoT devices from critical network segments.
Deploy DNS filtering to prevent exploit kit access.
Configure browser security policies blocking dangerous file types.
Implement WAF rules to detect CVE-2025-25257 exploitation attempts (T1190).
Short-Term Response (24-72 Hours)
Enhanced Detection and Response
Deploy behavioral analytics for ransomware detection (<15 seconds).
Implement endpoint detection tuned for AI-assisted attacks (T1566).
Configure SIEM rules for malicious HTTP payloads (T1071).
Monitor for suspicious browser processes and lateral movement (T1083).
Backup and Recovery Validation
Test backup integrity using air-gapped storage systems.
Validate incident response partnerships with specialized recovery firms.
Establish secure communication channels for sensitive operations.
Deploy deception technology to detect advanced persistent threats.
Medium-Term Planning (30-90 Days)
Architecture Enhancement
Implement zero-trust micro-segmentation for supply chain access (T1199).
Establish software composition analysis for JavaScript dependencies.
Deploy network monitoring for unusual IoT traffic patterns.
Implement least-privilege access for WordPress administrators.
Intelligence and Monitoring
Establish dark web monitoring for corporate data exposure.
Subscribe to CISA Cyber Alerts for nation-state threat intelligence (e.g., Salt Typhoon updates).
Audit supply chain vendors for exposure to Russian-linked entities (e.g., Cyber Resistance targets).
Implement enhanced due diligence for international technology partnerships.
Long-Term Strategic Positioning (90+ Days)
Resilience Building
Develop comprehensive threat models for nation-state actors.
Establish international cybersecurity partnerships and information sharing.
Implement board-level cyber risk governance frameworks.
Build comprehensive vendor risk management programs.
Intelligence Gaps and Monitoring Priorities
Critical Unknown Factors
Timeline for additional Chrome zero-day discoveries.
Full scope of WordPress supply chain compromise impact.
North Korean npm package campaign expansion plans.
Salt Typhoon persistence mechanisms in telecommunications infrastructure.
Potential for coordinated multi-vector attacks combining identified threats.
Enhanced Monitoring Requirements
Real-time browser exploit detection and blocking (T1189).
Supply chain integrity monitoring for software dependencies (T1199).
Nation-state TTPs tracking and attribution analysis.
AI-enhanced ransomware behavior pattern recognition (T1566).
Cross-sector threat intelligence sharing and correlation.
Conclusion and Call to Action
The cybersecurity landscape faces a perfect storm of critical vulnerabilities, sophisticated adversary capabilities, and geopolitical tensions. Exploitation timelines are measured in hours, requiring immediate action to patch vulnerabilities (e.g., CVE-2025-6558, CVE-2025-25257), enhance detection, and strengthen supply chain security. CISOs must secure executive commitment and emergency funding to ensure resilience, leveraging industry trends like MSSP consolidation and AI-driven investments to bolster defenses. Organizations demonstrating superior cyber resilience will emerge with strengthened market positions, while inaction risks catastrophic disruption.
Cyber Threats & Attack Trends
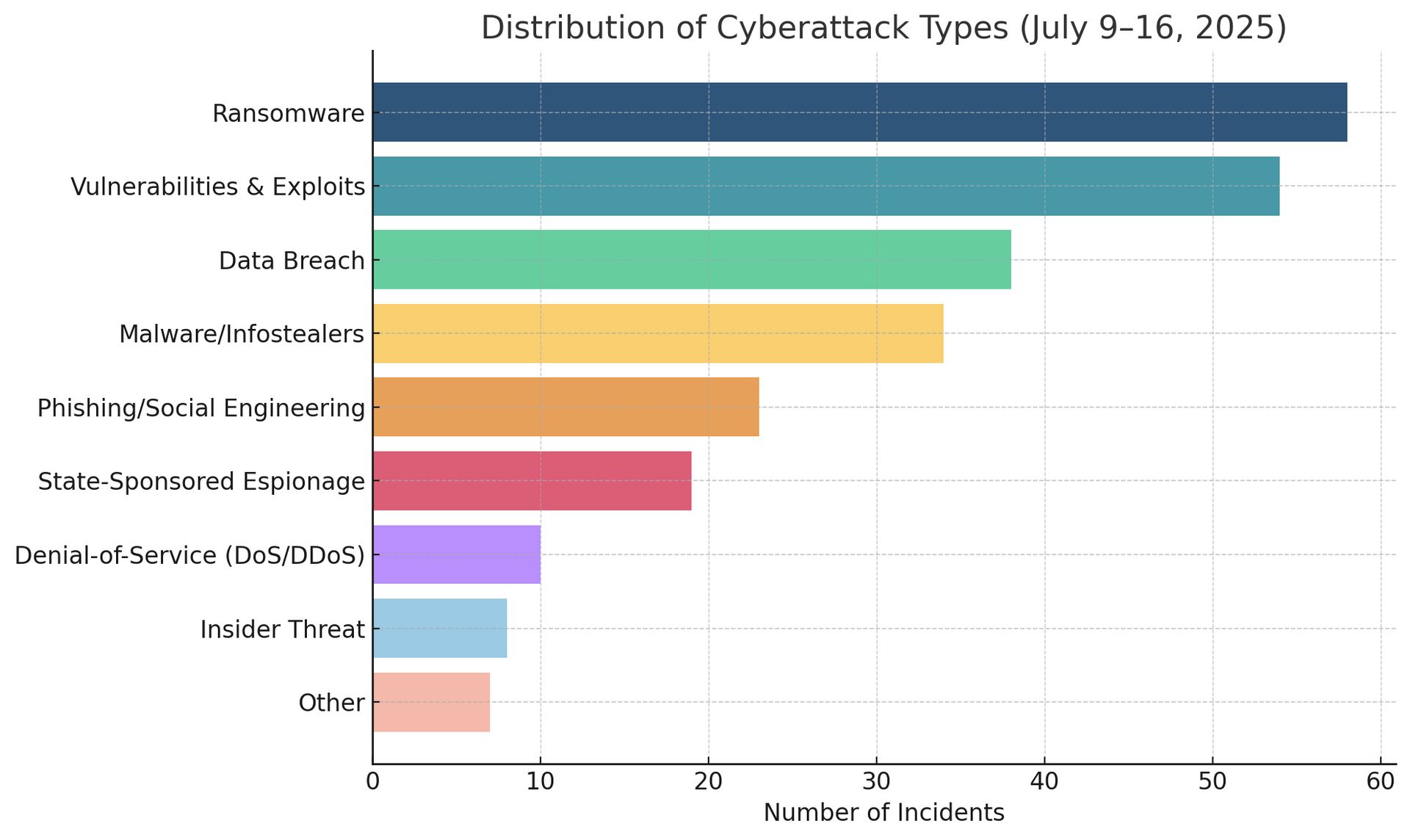
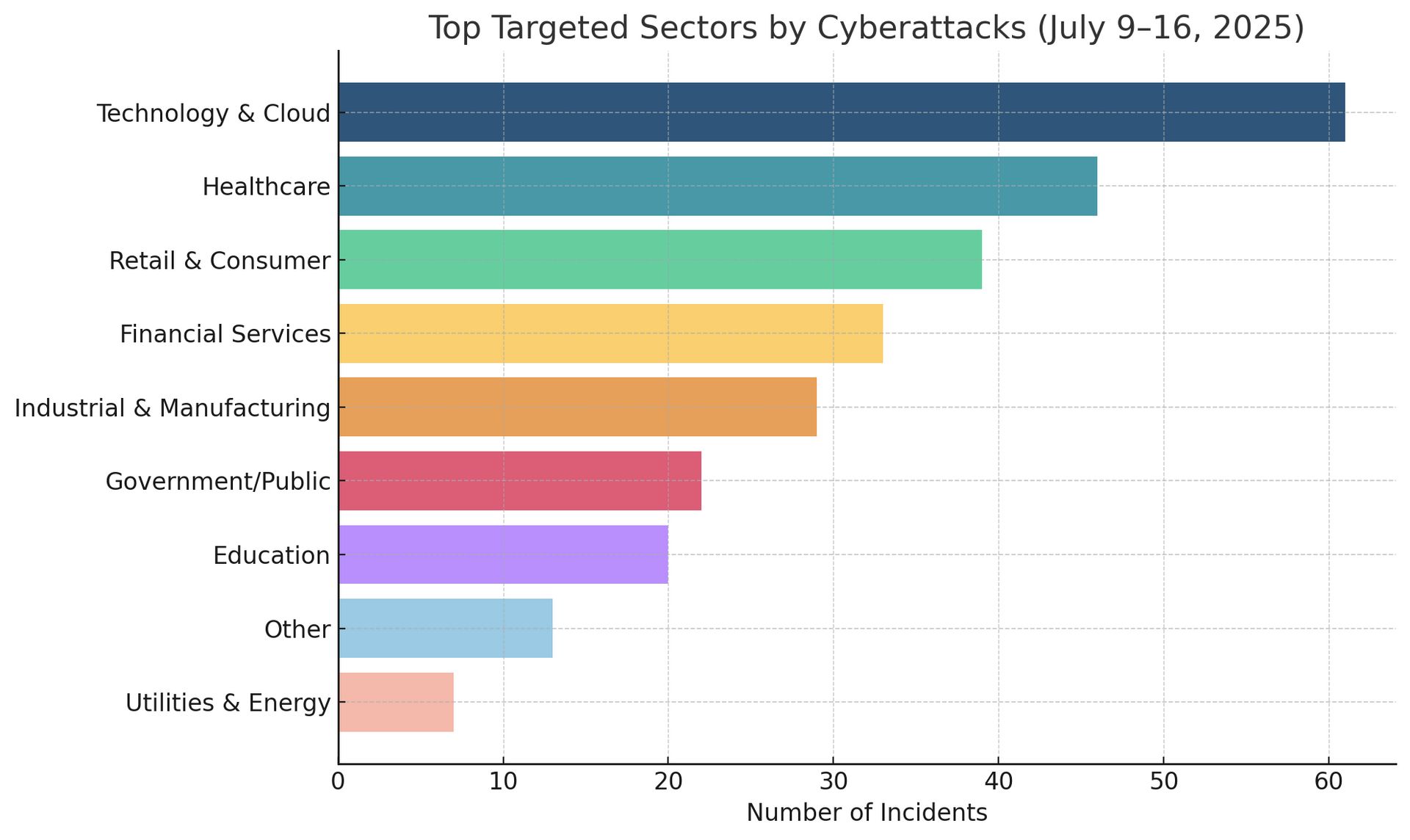
CybersecurityHQ: This Week’s Reports Based on Technical Research and Academic Papers
→ Free
When the machines stop talking: the critical infrastructure AI crisis nobody saw coming 👉 Read the report
→ Pro subscriber-only
Comparing the effectiveness of security frameworks in reducing infrastructure-as-code risks with minimal developer burden 👉 Read the report
Using blockchain to strengthen traceability and transparency in SEC cybersecurity disclosures 👉 Read the report
Enhancing information security: aligning internal controls with PCI DSS 4.0 in financial services organizations 👉 Read the report
And more inside - check out the full list here.
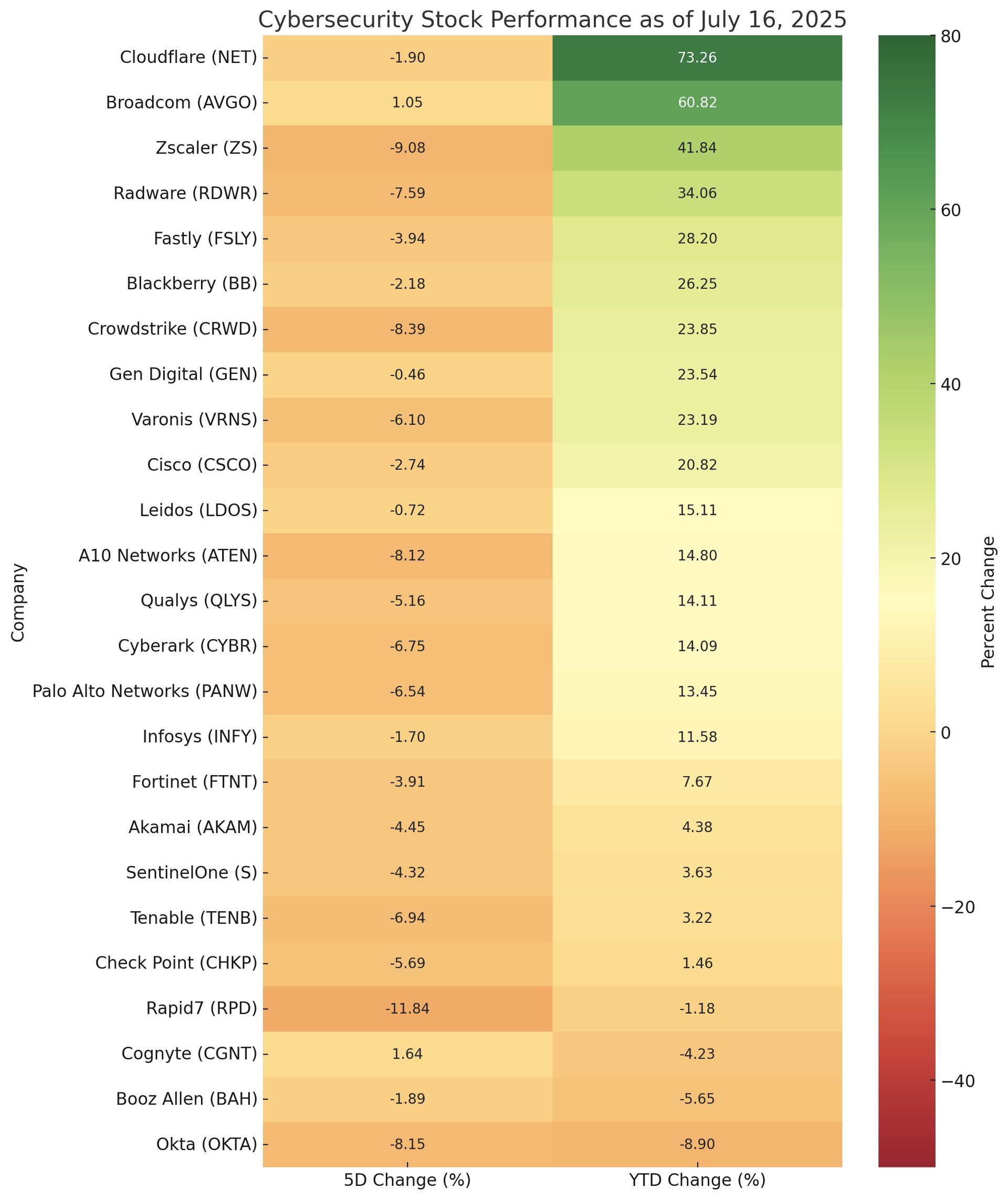
Cybersecurity Stocks
Cyber Intel Brief: Key Insights from Leading Security Podcasts
This is what you missed in this week’s Cyber Intel Report sourced from top cybersecurity podcasts and webinars, if you haven’t upgraded your membership:
⤷ OSINT Weaponization enables Sinaloa cartel FBI tracking while geolocation data predicts SEC investigations through democratized surveillance
⤷ 1.7% Training Failure exposes awareness program catastrophe as 46% continue password reuse despite cultural security investment failures
⤷ Skills Gap Myth reveals hiring dysfunction through eight-stage interviews and unrealistic requirements eliminating qualified candidates from cybersecurity roles
⤷ 2030 Quantum Deadline approaches for post-quantum migration as RSA encryption becomes obsolete with 50% quantum probability by 2039
⤷ Shadow Brokers Legacy continues WannaCry/NotPetya global damage as intelligence failures kill patients without public accountability
⤷ Netflix Culture Excellence prevents major incidents through employee empowerment and shared responsibility model driving security transformation
And more insights in this week’s full CISO briefing.
Interesting Read
UN calls for global action against AI-driven deepfakes
On July 11, the United Nations’ International Telecommunication Union (ITU) released a report urging international cooperation to combat the growing threat of AI-generated deepfake content. The report highlights how deepfakes are increasingly used to spread disinformation, manipulate public opinion, and facilitate financial fraud and geopolitical destabilization.
It calls for platform-level detection tools, digital watermarking standards, and provenance metadata to verify the authenticity of audio, video, and images. The UN warns that fragmented global standards are creating enforcement gaps that adversaries are actively exploiting.
Why CISOs care: Expand tabletop scenarios to include deepfake threats, assess existing controls for validating audio and video content, and join working groups focused on provenance standards and multimedia authentication infrastructure.
Fresh From the Field: Security Resources You Can Use
Title | Publisher / Authors | Focus | Access Link |
|---|---|---|---|
Cybersecurity and Financial System Resilience Report 2025 | Federal Reserve Board | U.S. financial-sector cyber risk management, AI/cloud resilience, third-party oversight, and systemic incident coordination | |
Preliminary Considerations for Multi‑Directional Sharing of SCRI | CISA | Explores legal and policy frameworks to enable secure exchange of Sensitive Cybersecurity-Related Information between enterprises and government | |
State of Cybersecurity Resilience 2025 | Accenture | Economic model linking security investment to resilience; includes ROI insights and organizational trust metrics | |
Asymmetry by Design: Boosting Cyber Defenders with Differential AI Access | Shaun Ee et al. | Proposes frameworks giving defenders privileged AI tools to preserve cyber advantage—high relevance for red/blue team strategy | |
From Texts to Shields: Convergence of LLMs & Cybersecurity | Tao Li et al. | Investigates deploying LLMs in vulnerability discovery, generative defense, trust, transparency, and human-in-loop design |
Fortinet
Atlanta, GA, US
Palo Alto Networks
Santa Clara, CA, US
Booz Allen
Colorado Springs, CO, US
RTX
Remote (Katy, TX, US)
TalentAlly
Northampton, MA, US
Datadog
New York, NY, US
Sr. Manager, Cybersecurity & Compliance
Fairlife
US, IL, Chicago
Gen3 Technology Consulting
Remote (Baltimore, MD, US)
Fractional CISO (Part-Time, Contract)
Trunk Tools
Remote (San Francisco, CA, US)
Stay safe, stay secure.
The CybersecurityHQ Team


Reply